📗 -> 04/21/25: ECS189G-L10
sec_6_auto_encoder.pdf - Google Drive
🎤 Vocab
❗ Unit and Larger Context
Autoencoders
- Auto-encoders are a family of neural network with two main components:
- Encoder: Compress the input x into low-dimensional embedding representation z
- Decoder: Reconstruct the input x’ from the embedding representation z
- Loss Function: minimize the difference between x and x’, so as to train the encoder and decoder concurrently
- Highlights: Auto-encoders work in an unsupervised manner, no supervision label information will be needed
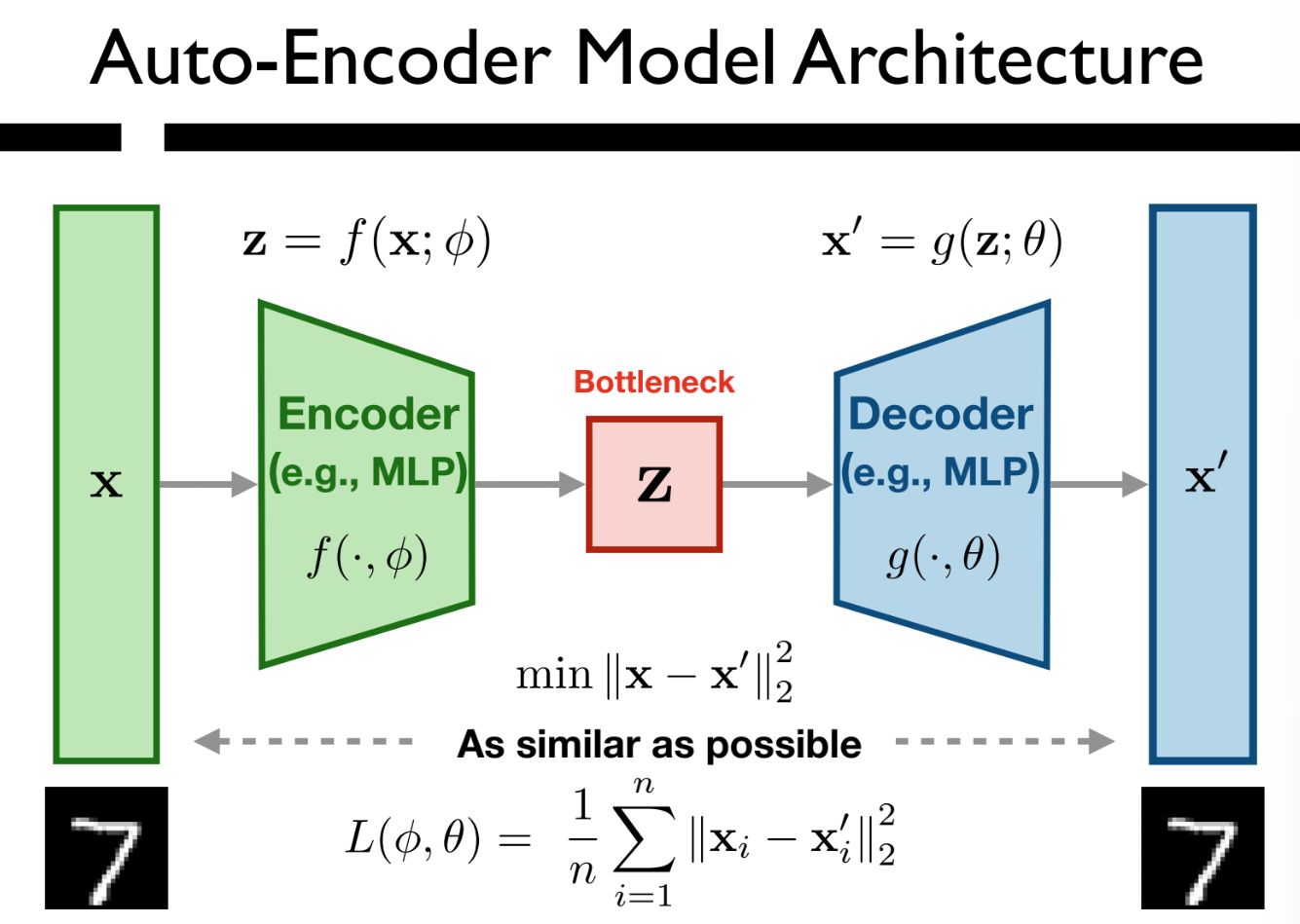
- Notice the structure:
- Encoder -> Bottleneck -> Decoder
- Bottleneck Dimensions:
- Notice the loss:
- Calculating the squared Euclidean distance between each instance of original to reconstructed, and then averaging
- Squared because it makes math easier?
- Calculating the squared Euclidean distance between each instance of original to reconstructed, and then averaging
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
Applications of an Auto-Encoder
- Input Embedding: Map high-dimensional data into lower dimensional representations for learning and visualization
- Data reconstruction: it enables data reconstruction and generation based on the (noisy or dirty) inputs
- Data compression: it can reduce the size of dataset (files) effectively without much information loss
- We can reconstruct the inputs with the embeddings
- Unsupervised representation learning: it doesn’t require label information for representation learning
- Can be widely used in model pre-training
Potential Applications:
RNN Encoding
- Speech Recognition
- Language translation
Others: - Image Processing
- Anomaly Detection
- Recommender Systems
- Information Retrieval
- etc.
Can Also do other things!
Image Style Transfer with Auto-encoder Architecture
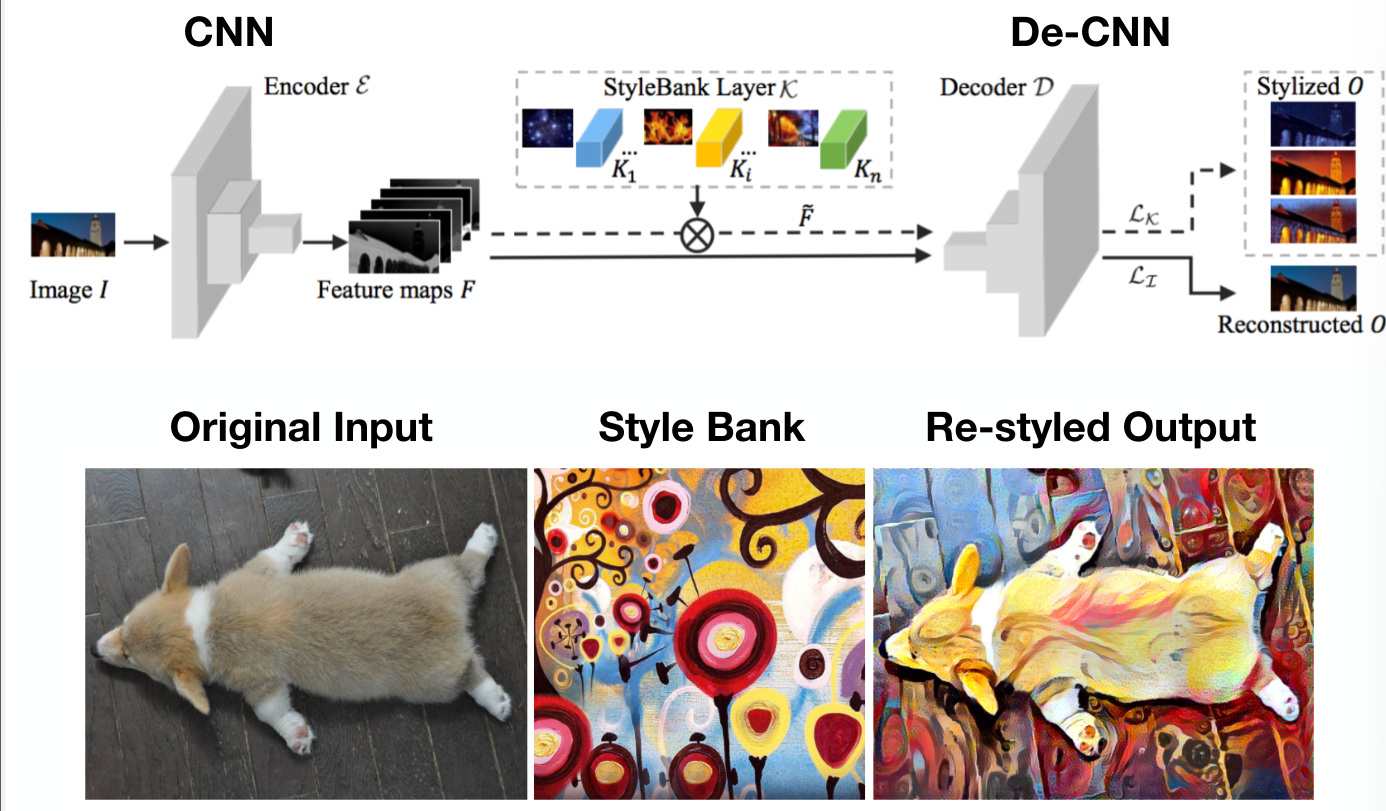
- Minimizing 2 loss functions:
- Making encoded representation as accurate as possible
- Making style output as accurate as possible
Quick Review
Lp-norm
- p=1, 2, …, infty
Regulatization: - Ridge Regression
- Has an optimal solution
- Lasso Regression
- Not differentiable and no closed form solution but can be addressed by subgradient methods, least-angle regresson, and proximal gradient methods
Regularizing the auto encoder is important so that it carries general information about the data, and doesn’t overfit to the training set.
- Not differentiable and no closed form solution but can be addressed by subgradient methods, least-angle regresson, and proximal gradient methods
- Better fit/more robust
Regularized Auto-encoders
How to guarantee the bottlenck embedding carries information?
Will be meaningless. No bottlenecking Will bog down model capacity
Instead of tuning the bottleneck size manually, we choose to tune its sparsity instead. Regularization Term:
Derivative Penalty
- Generated by a corruption function, adding noise
- Forces the model to learn a function that doesn’t change much when x changes slightly
De-Noising auto-encoder
- M is a stand in for a corruption function,
being the noised x
- M is a stand in for a corruption function,
- Could consider doing knockout as a corrupter
Ideally, the generation of the autoencoder would be identical to, the uncorrupted input, despite the autoencoder being inputted
🧪 -> Refresh the Info
Did you generally find the overall content understandable or compelling or relevant or not, and why, or which aspects of the reading were most novel or challenging for you and which aspects were most familiar or straightforward?)
Did a specific aspect of the reading raise questions for you or relate to other ideas and findings you’ve encountered, or are there other related issues you wish had been covered?)
🔗 -> Links
Resources
- Put useful links here
Connections
- Link all related words