Q1
Q2
Q3
Motor representation of words in the brain:
- Lemma
Q4:
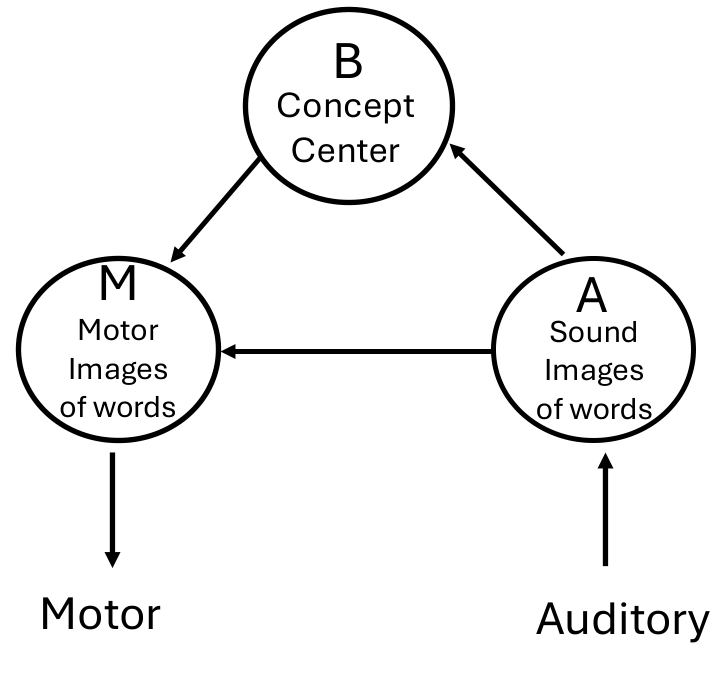
According to the Wernicke model, which represents word meaning?
- B / Wernicke’s
Q5:
If there was damage that disconnected the conceptual center from the motor area, what would happen?
- Conduction aphasia, difficulty repeating words
Q6:
A patient struggles to nderstand sentences with complex grammar, such as those with passive voice.
They likely have issues with:
- Closed-class words
Q7:
A patient has trouble with speech, sounds effortful
- Broca’s aphasia
Q8:
Test a patients ability to distinguish between similar speech sounds, a clinician would use:
- Phoneme discrimination task
Q9:
Where is language processed?
- Mostly left, but definitely BOTH are INVOLVED
Q10:
Which statement about the hickok and peopel model is true?
- The dorsal pathway is involved in auditory motor integraion
On the test
MANY QUESTIONS ABOUT HICKOK AND PEOPEL MODEL
study it, be familiar with each part
Q11:
In spoken language comprehension, the component that links the sound structure of a word to its meaning is the:
- Lexical interface
Q12:
The existence of diverse sign languages mean:
- Signed languages develop naturally within deaf communities
Q13:
How might sign language representation in the brain differ from spoken language representation?
- Sign language does not involve a lexical interface
- They don’t interface word->speech, but word->hand.
- It different?
Q14:
A scientifi theory:
- A principled theory…
Q15:
Which of the following statements about research and theories in neurolingusitcs is true:
- There is not univesal agreement among linguistics
Q16:
The dorsal pathway in the brain connects the:
- Temporal and parietal
Q17:
In the hickok and peoppel model, the middle temporal gyrus would be considered the:
- Lexical interface
Q18:
Why adults might find picking a language up harder than children?
- Adults are beyond the critical period
Q19
If a child learns two languages from birth, with each parent speaking a different language, is mot likely a/an:
- Compound bilingual
Coordinate is when you learn one at school, and another at home
Q20:
Which of the following statements about bilingual aphasia is NOT always true?
- Something about double negative confusion when writing the question?
- The takeaway was: not as predictable
- All recovery options are possible, they could lose one but not another, neither, etc.
Q21:
What factor contributes to similar brain activation patterns in bilinguals
- Language proficiency
Q22:
Q23:
Speech error where a word is subbed in with a word similar in sound called:
- Phonemic paraphasia
Q24:
Neuroprosthetic device in the article:
- Restored speech in ALS
Q25:
What does it require to work:
- Neural signals and decoding networks
Q26:
damage to what can result in fluent aphasia
- Temporal lobe
Q27:
What does ‘lemma’ refere to in language processing models?
- Meaning of a word
Q28
According to two stream model, dorsal stream is primarily involved in:
Q29:
Lesion -> fluent aphasia
- Wernickes
Q30:
Double dissocciation suggests
- Different brain areas responsible for different functions
Q31:
Dual stream, ventral stream associated with
- Sounds to meaning mapping
Q32:
Lexical interface:
- Linking sound patterns to meaning
Q33:
Diff in neural representaion of signed and spoken language
- Sign language involves more spatial processing
Q34:
Connections between parietal and frontal lobes are crucial for
- sensorimotor integration
Articulatory network:
- Planning and executing speech movements
Critical period suggests:
- Sensitive period for language acquisition
Synaptic pruning in the brain:
- Decreases with age
Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI) programs emphasize:
- Screening newborns for hearing loss
Antagonistic recovery in bilingual aphasia refers to:
- One language improving while the other worsens
Anomia:
- Difficulty finding words
The neuroprosthetic study showed:
- ways to improve quality of life for people with paralysis