Linguistics 175 - Quiz 2
1. Neuroimaging Techniques
- Spatial vs. Temporal Resolution
- Know the different “sizes” of spatial resolution:
- Cortical regions - Larger, more corresponding to lobes
- Brodmann’s areas - Smaller, areas 44 & 45 correspond to broca’s area.
- Single cell recording - Record as small as neurons.
- Know the different “sizes” of spatial resolution:
- Comparison of Techniques:
- MRI
- Detects blood flow changes
- Pros: Spatial resolution, non-invasive
- Cons: Temporal resolution
- PET
- Tracks movement of radioactive tracer
- Pros: Good spatial resolution
- Cons: Invasive (tracer) and lower temporal
- MEG
- Measures magnetic fields produced by brain
- Pros: Temporal resolution, non invasive
- Cons: Not great spatial resolution, susceptible to movement
- ERP (Event-Related Potentials)
- Electrical activity on the scalp
- Pros: Temporal resolution, non invasive, cheap
- Cons: Bad spatial resolution, noisy
- NIRS (Near-Infrared Spectroscopy)
- Measures change in blood oxygenation using near-infrared light
- Pros: Inexpensive, portable, non invasive
- Lower spatial and temporal resolution
- ECOG
- Electrodes placed on the brain
- Pros: High spatial and temporal resolution
- Cons: Very invasive
- Neuropsychological testing/Lesion studies
- Examines cognitive capabilities using tasks
- Pros: Some of our biggest insights
- Cons: Not as scientific or controlled
- MRI
- Spatial:
- MRI > MEG > PET > NIRS > ERP
- Temporal:
- MEG=ERP > fMRI > PET > NIRS
- Populations:
- fMRI can’t be used for people with metal implants very well
- Claustrophobics no scanners
2. Brain Damage & Neuropsychological Testing
- Double Dissociation
- Neuropsychological testing,
- Potential impacts of tumor resection on language function
- Post-surgical neuropsychological testing
- Aphasia vs. Apraxia
3. Brain Stimulation & Cognitive Recovery
- Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS)
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
4. Cognitive Neuroscience Methods
- Subtractive Logic in MRI
- Experimental Design Considerations
- What factors are important in deciding whether the results of a study support your theory?
- Purpose of peer-review journals
5. Classical Models of Language Processing
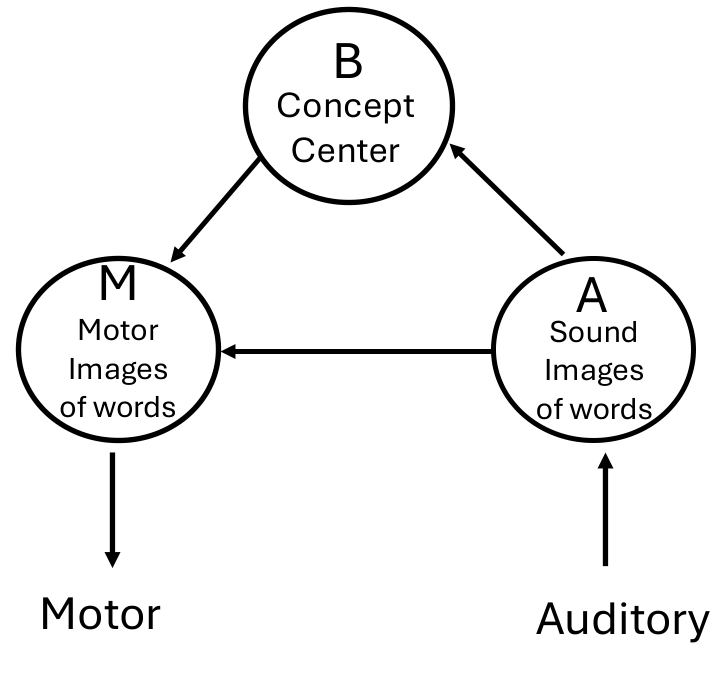
-
Wernicke-Lichtheim-Geschwind Model:
-
Ventral and Dorsal Pathways - Milner and Goodale (1995)
- Ventral Stream - What.
- “The transformations carried out in the ventral stream permit the formation of perceptual and cognitive representations which embody the enduring characteristics of objects and their significance”
- Dorsal Stream - How/Where
- “concerned only with the observer’s actions within the visual world. The transformations carried out in the dorsal stream, mediate the control of goal-directed actions”
- Ventral Stream - What.
-
What and Where in Language:
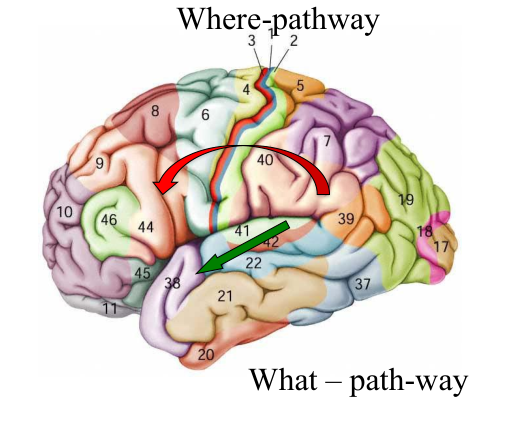
- Ventral Pathway
- Lexical Conceptual processing (Wernicke’s)
- Dorsal Pathway
- Sensori-motor/articulation (to Broca’s)
- Doing things with language
- Ventral Pathway
-
Hickok & Poeppel Model:
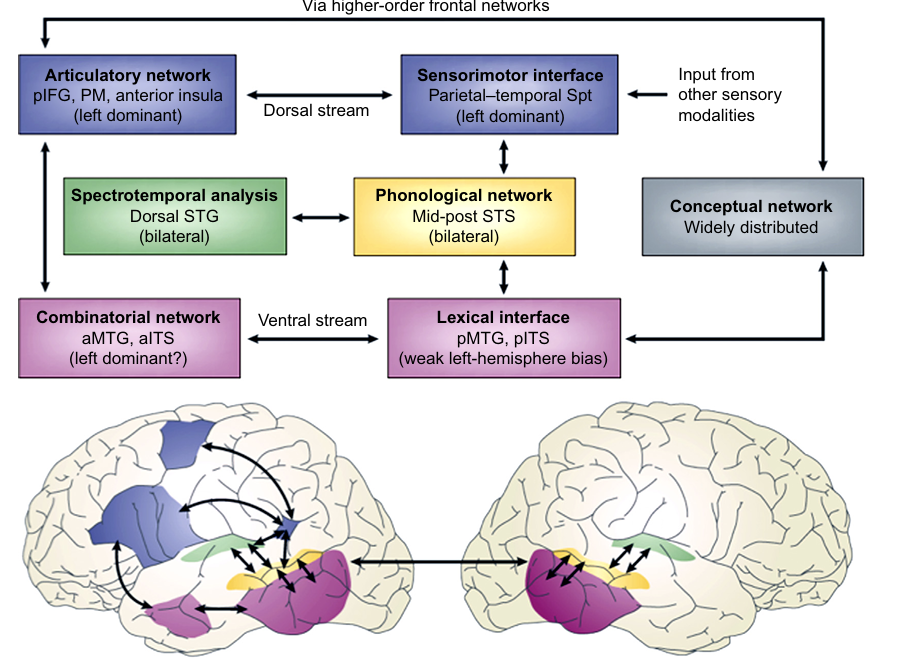
-
Purple is the ventral stream
- Maps the sound structures of words onto the corresponding semantic representations
- Contributes to forming the integrated meanings of complex utterances like phrases and sentences
-
Dual stream vs single stream models
-
Review homework 3
Lemma Model:
- Two stages of lexical selection
- Lexical selection:
- Conceptual focusing perspective-taking
- Lexical concept
- Lemma selection
- Lemma
|
\/
- Lexical selection:
- Three stages of form encoding
- Form encoding:
- Retrieving morphemic phonological codes
- Phonological codes
- Prosodification syllabification
- Phonological word
- Phonetic encoding
- Articulatory score
- Form encoding:
6. Visual & Auditory Processing
- Visual Field Processing:
- Left visual field → right hemisphere
- Right visual field → left hemisphere