📗 -> 01/07/25: NPB162-L1
🎤 Vocab
Ethology: The biological discipline that studies natural animal behavior in a broad range of organisms by using objective and comparative approaches.
Neuroethology: The biological discipline that attempts to understand how the nervous system controls the natural behavior of animals
❗ Unit and Larger Context
Lecture 1 Outline
-
Tinbergen’s four questions
-
What is Neuroethology?
- Choosing a simple model system
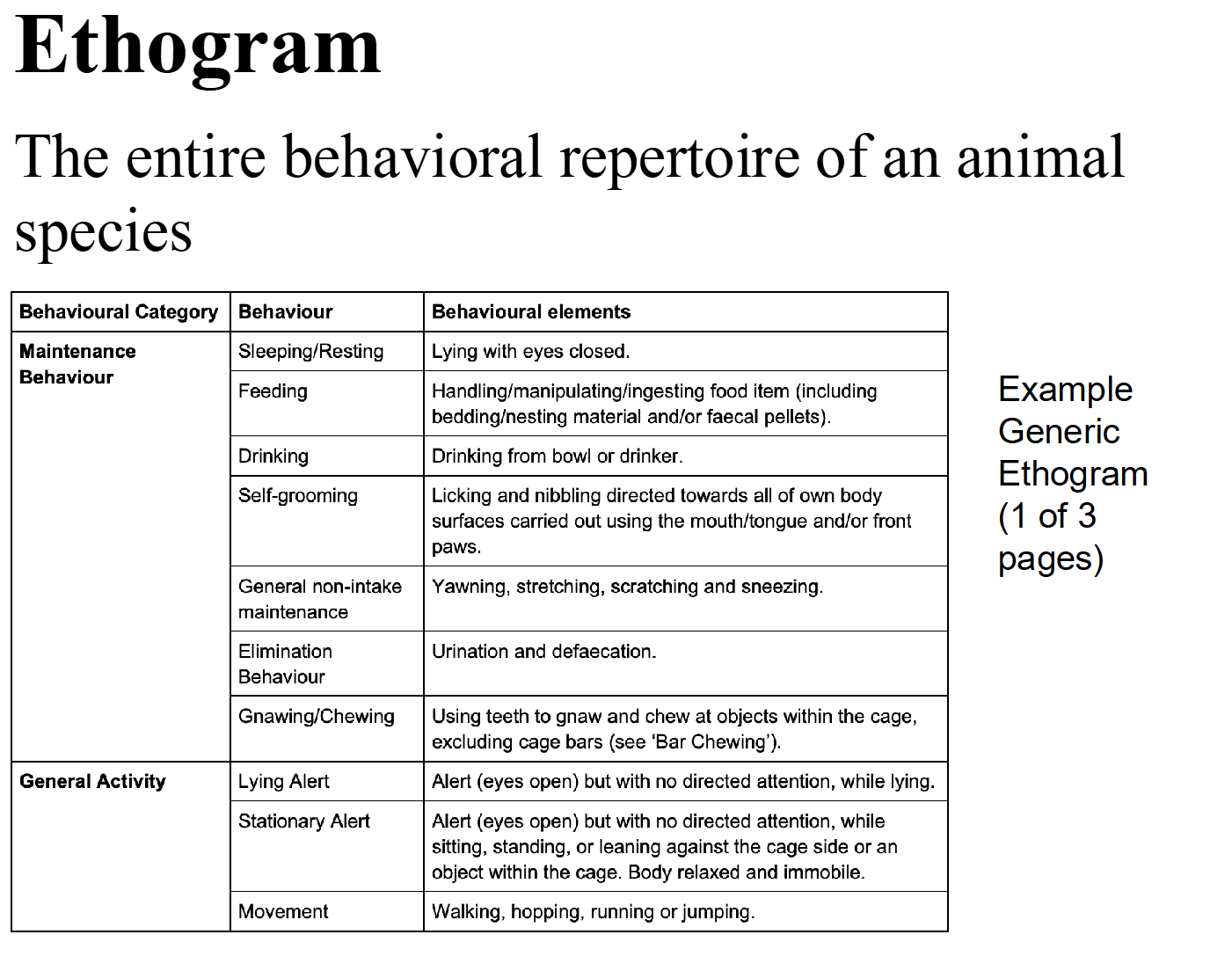
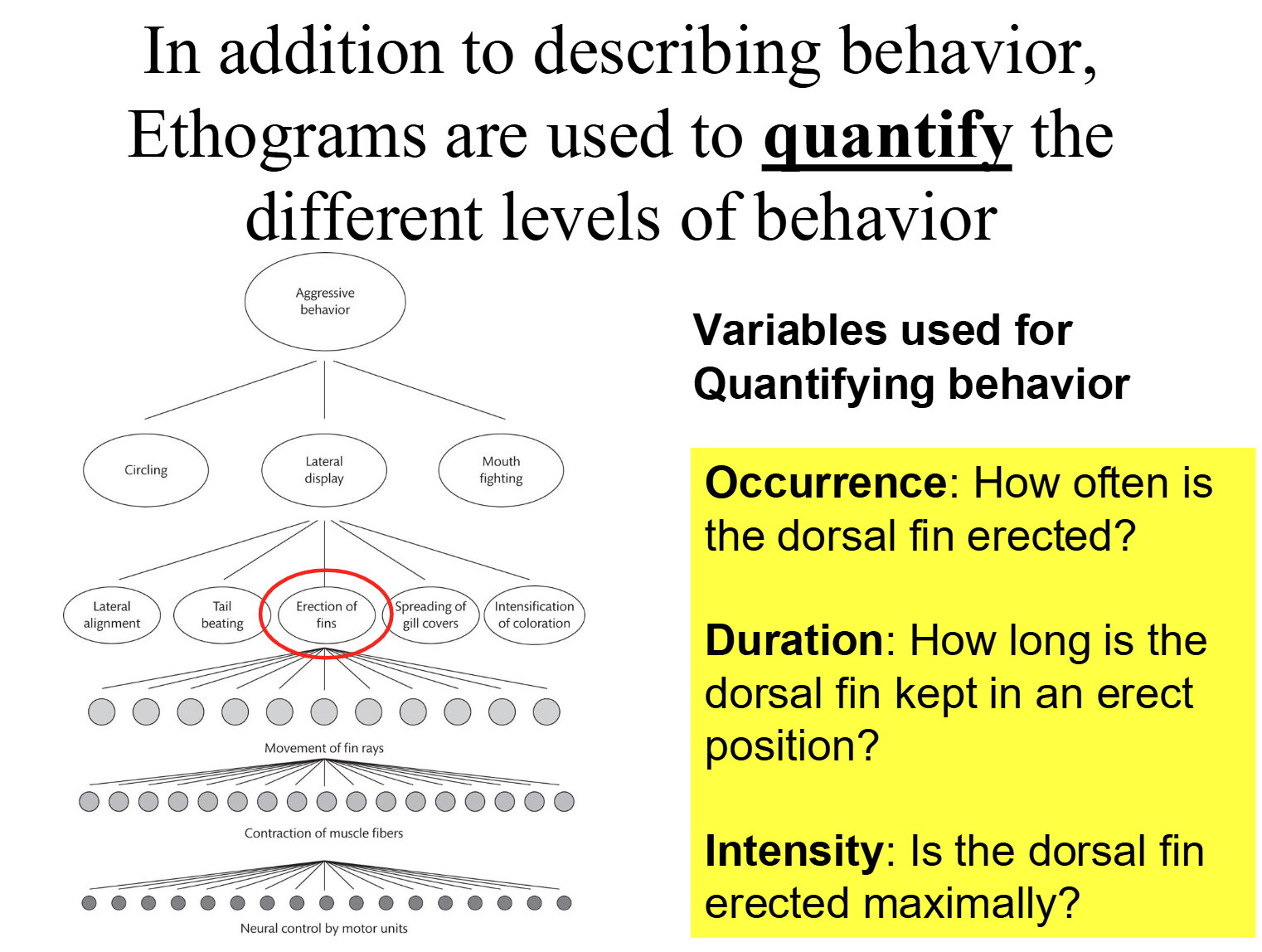
- Ethogram: The entire behavioral repertoire of an animal species
-
Innate behavior vs Learned behavior
- Fixed Action Pattern (FAP)
- Learned behavior
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
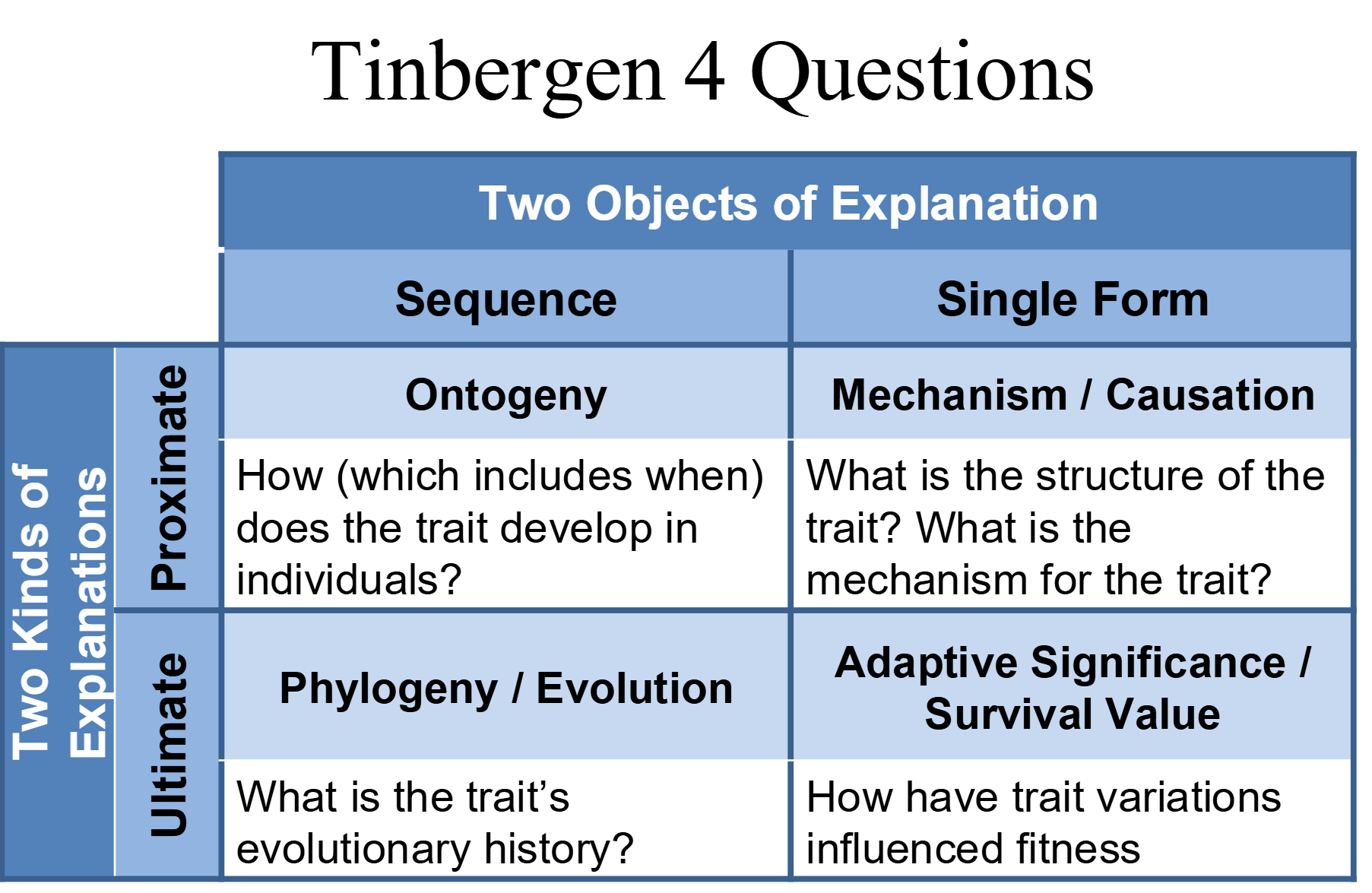
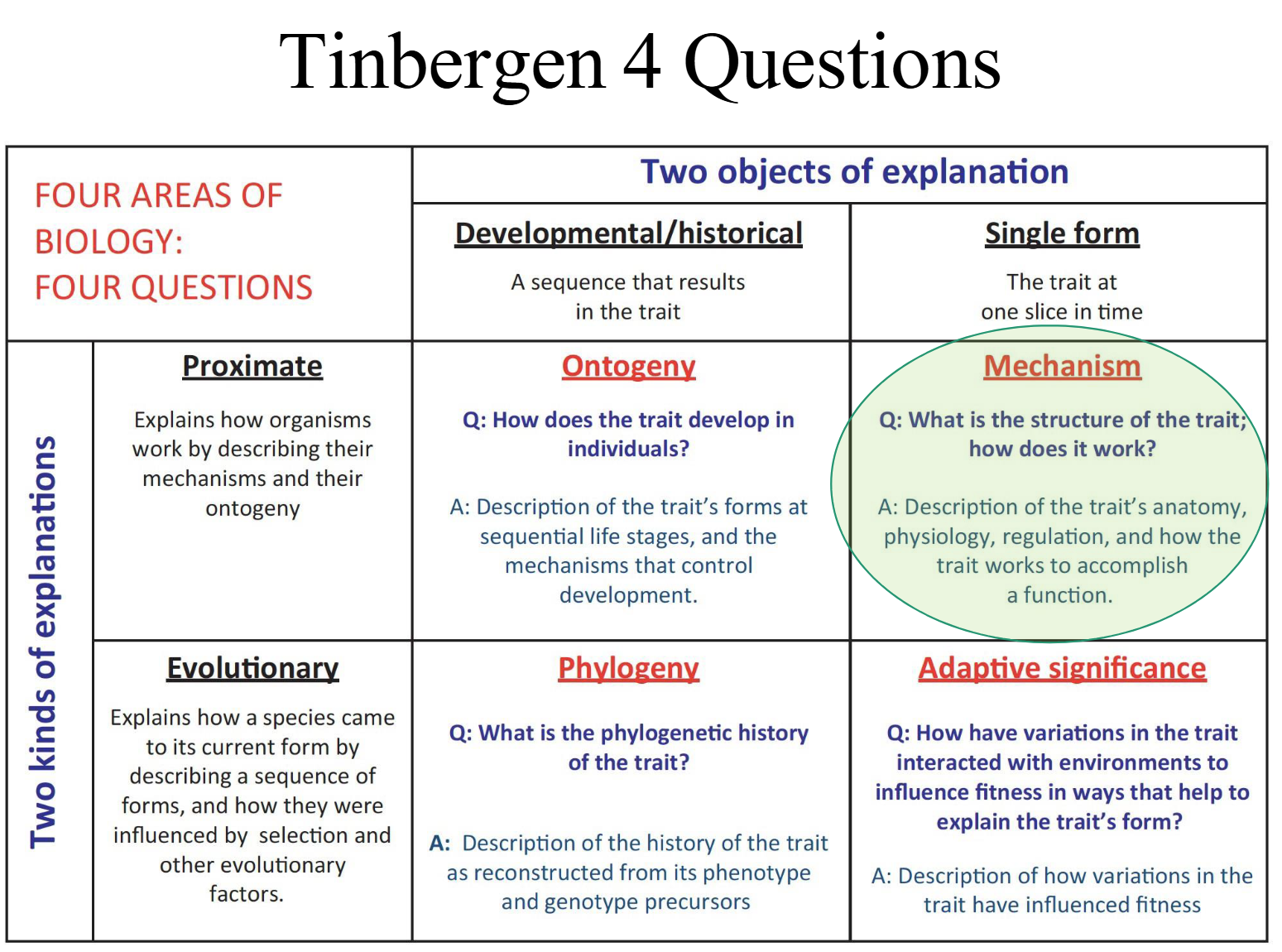
Tinbergen’s Four Questions
A framework for analyzing behavior
- Function (or adaption): Why is the animal performing the behavior?
- Evolution (or phylogeny): How did the behavior evolve?
- Causation (or mechanism): What causes the behavior to be performed?
- Development (or ontogeny): How has the behavior developed during the lifetime of the individual?
Questions 1 and 2 give ultimate or evolutionary explanations. These are answers that take a longer perspective and try to explain why the behaviour has evolved.
On the other hand, questions 3 and 4 give proximate explanations. These are answers that look into the immediate mechanical reasons for why a behavior is expressed.
 |  |
|---|
Cichlid behavior is an example of a well studied species with highly developed behaviors.
Krogh’s Principle:
- “For a large number of problems there will be some animal of choice or a few such animals in which it can. Be most conveniently studied”
Possible exam question:
What makes an animal ideal for study?
- Inexpensive
- Suitable for lab study
- Easy to maintain
- Easy to breed
- Lots of kids
and other relevant behaviors! (lifespan, simplicity)
Innate Behavior
Unlearned behavior. Instinctive.
- reflexes
- taxis
- kinesis
- fixed action patterns
- circadian rhythms
- …
Fixed Action Patterns (FAP)
- complex behavior with a lot of steps
- continues despite interruption
- Innate
Example - Egg rolling behavior in a chicken. It will attempt to bring egg to nest, but if egg taken they will continue rolling the ‘egg’
Once triggered, you cannot stop them.
Sign Stimulus - Triggers the FAP.
- Presenting egg to chicken
- Releasing Value - Property of stimuli of how strong/reliable it is in inducing the FAP
Innate Releasing mechanism - Hardwired neural network in the brain, that triggers a particular response
Applications: You can measure the releasing value of an egg, by how reliably it triggers FAP.
- Greener egg > Browner egg
- Larger egg > Smaller egg
Learned Behavior
Behavior developed through experience
- Imprinting
- Habituation
- Sensitization
- Classical Conditioning
- Operant Conditioning
- …
Konrad Lorenz, Niko Tinbergen and Karl Von Frisch shared the Nobel Price in 1973 (1886 - 1982)
- “Discoveries in individual and social behavior patterns”
Classical Conditioning:
Learned association
- US: Unconditioned Stimulus
- UR: Unconditioned Response
- CS: Conditioned Stimulus
- CR: Conditioned Response
Operant Conditioning / Procedural Learning
- Positive Reinforcement
- Positive Punishment
🧪 -> Refresh the Info
Did you generally find the overall content understandable or compelling or relevant or not, and why, or which aspects of the reading were most novel or challenging for you and which aspects were most familiar or straightforward?)
Did a specific aspect of the reading raise questions for you or relate to other ideas and findings you’ve encountered, or are there other related issues you wish had been covered?)
🔗 -> Links
Resources
- Put useful links here
Connections
- Link all related words