📗 -> 03/11/25: Navigation
🎤 Vocab
❗ Unit and Larger Context
20 mins late
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
Spatial maps in the hippocampus:
- place cells
Abrupt phase transition between square-
like and circle-like representations in
intermediate octagonal environments.
Place cells are not metric - they do not preserve distances
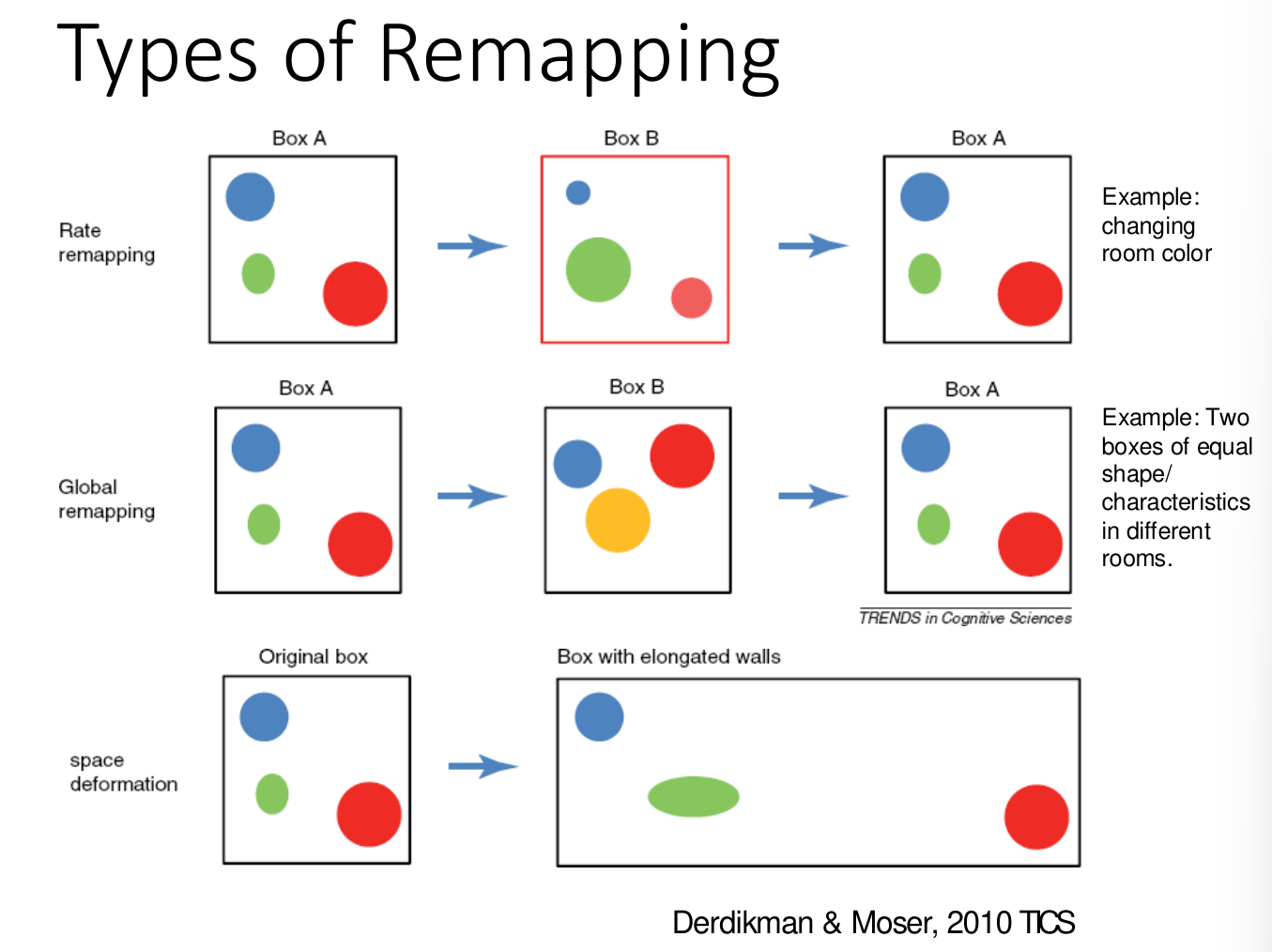
Types of Remapping:
- Rate Remapping
- Global Remapping
- Space deformation
Not just space information:
- Place cells can fire in anticipation of a turn in a given maze
- “Neurons that fire when rat is planning to turn left, instead of right. Encode some form of behavioral intention”
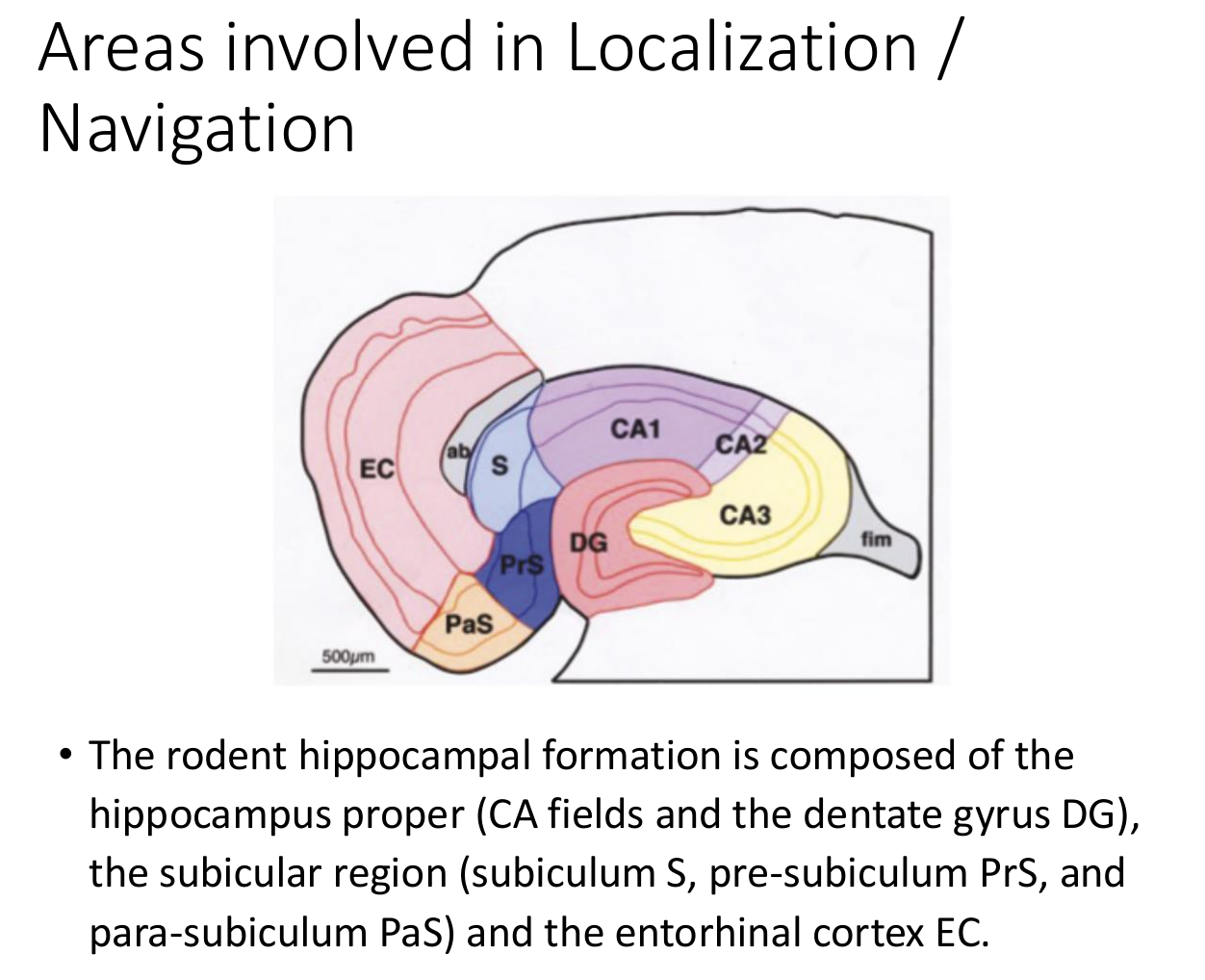
Spatial maps outside the hippocampus:
- grid cells, head-direction cells, border cells
Head Direction Cells:
- Navigation requires both a map of space and a compass to tell direction
- Head direction specific cells discovered James Ranck (1984) in dorsal presubiculum (also called postsubiculum)
- They remap, but they remap together (in relation to each other)
Time Cells:
- More complicated experiment, multiple designs/controls
- Find neurons responsive to time
Speed Cells:
- Most complicated experiment: Put rats in a little car, and see their neural response
- Find neurons responsive to running speed of car.
Grid Cells:
- Hexagonal coding of position
- Aligned to environment specific landmarks (same as place cells)
🧪 -> Refresh the Info
Did you generally find the overall content understandable or compelling or relevant or not, and why, or which aspects of the reading were most novel or challenging for you and which aspects were most familiar or straightforward?)
Did a specific aspect of the reading raise questions for you or relate to other ideas and findings you’ve encountered, or are there other related issues you wish had been covered?)
🔗 -> Links
Resources
- Put useful links here