📗 -> 04/01/25: NPB173-L1
[Lecture Slide Link]
🎤 Vocab
❗ Unit and Larger Context
Small summary
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
Importance of Brain Health
Responsible for the remarkable variety of human thought, action, and behavior
Complex system (>80 bill neurons and >100 trill synapses)
Dramatic changes across the lifespan
Impacts of brain disorders
Over 50 million Americans with disorders of brain functions
Estimated cost to US economy around 1.5 trillion per year
- Over 1000 different known disorders of brain function
Impact depends on severity, which varies across larger range
WHO estimates that brain disorders account for about one third of all years lost to death and disability from all diseases globally
Types of Brain Disorders
Distinction between Neurological and Psychiatric disorders
- A lot of the distinction comes down to treatment. Which is most useful in treating the disorders?
- Names come from the fields that tend to treat them.
- Not necessarily a fundamental difference
Neurology:
- Meningitis
- Epilepsy
Psychiatry: - Schizophrenia
- Mania
Others are more grey: - Mental retardation
- Autism
Understanding brain disorders
Symptoms: First person subjective observations by patient related to abnormal state
Signs: Third person objective indication or measurement related to abnormal state
- Ex: Body temperature
Diagnosis: Determination of what condition causes signs and symptoms
Pathophysiology: How processes have gone awry within an individual with an abnormal state
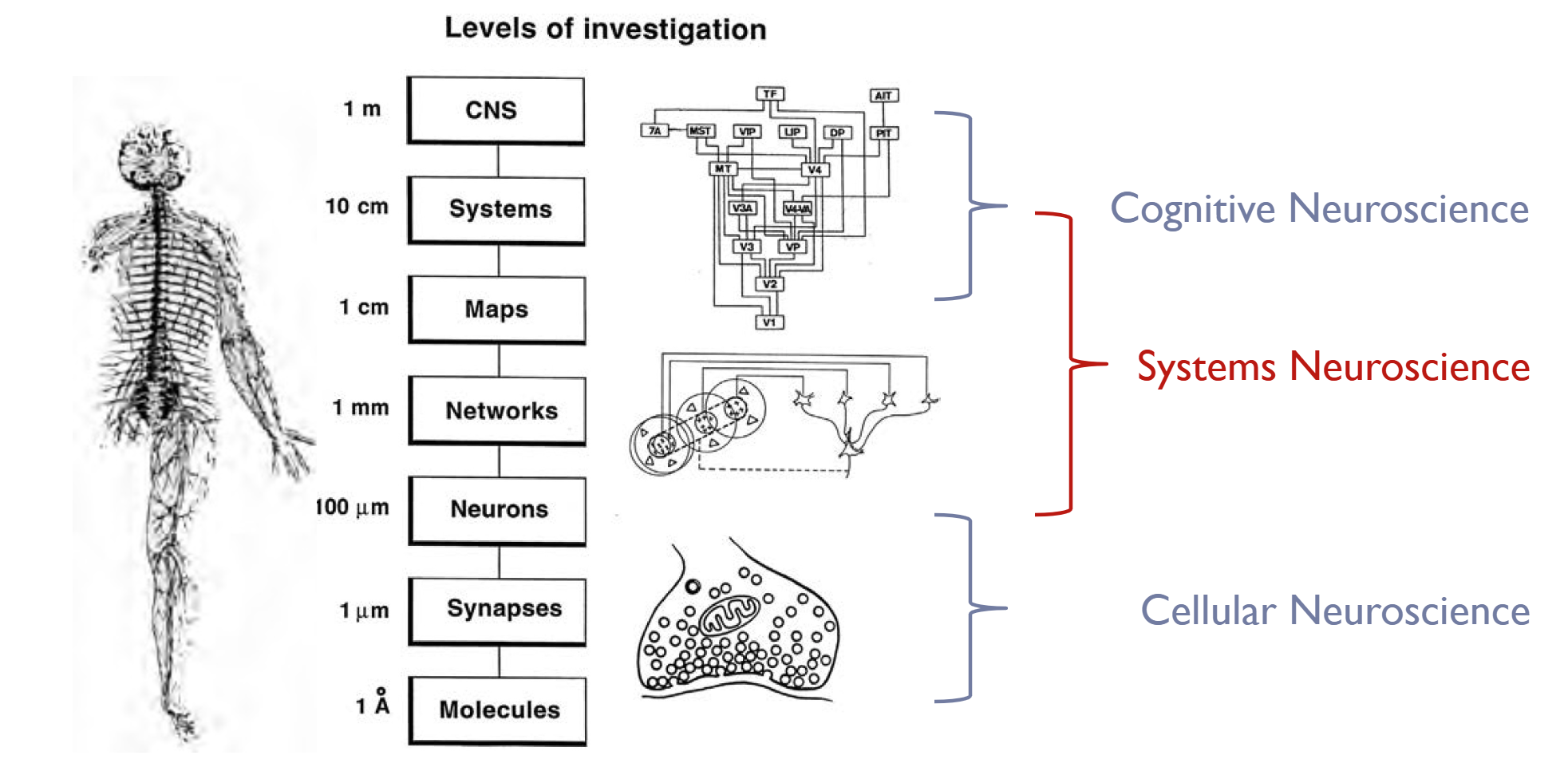
- This class will highlight the importance of connecting across levels
Treatment:
Multiple dimensions to consider:
- Invasiveness (non-invasive / invasive)
- Accuracy (targeted / global)
- Targeted if it has an isolated effect on the root cause
- Global if it is more general (side effects)
Studying brain disorders:
See effects in patients (Alzheimer’s brain’s being damaged IE)
Understand healthy brains to reference
Create model systems
- In vitro models
- In vivo models
Out the 40 neuroscience Nobel prizes, only 2 came from human subjects. The other 38 came from animal models. Knowledge shown to generalize across mammalian systems.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the impact of brain disorders
- Studying brain disorders for the complementary perspectives of neurology and psychiatry
- Characterizing signs and symptoms of dysfunction to read a diagnosis
- What is meant by pathophysiology
- Connecting across multiple spatial scales/levels of analysis of the nervous system
- Changing perspective from diseased brain to healthy brain as goal
- Use of model systems to better understand brain disorders.
🧪 -> Refresh the Info
Did you generally find the overall content understandable or compelling or relevant or not, and why, or which aspects of the reading were most novel or challenging for you and which aspects were most familiar or straightforward?)
Did a specific aspect of the reading raise questions for you or relate to other ideas and findings you’ve encountered, or are there other related issues you wish had been covered?)
🔗 -> Links
Resources
- Put useful links here
Connections
- Link all related words