📗 -> Motor Control and Learning
🎤 Vocab
❗ Unit and Larger Context
Now, talking a dive into the motor learning
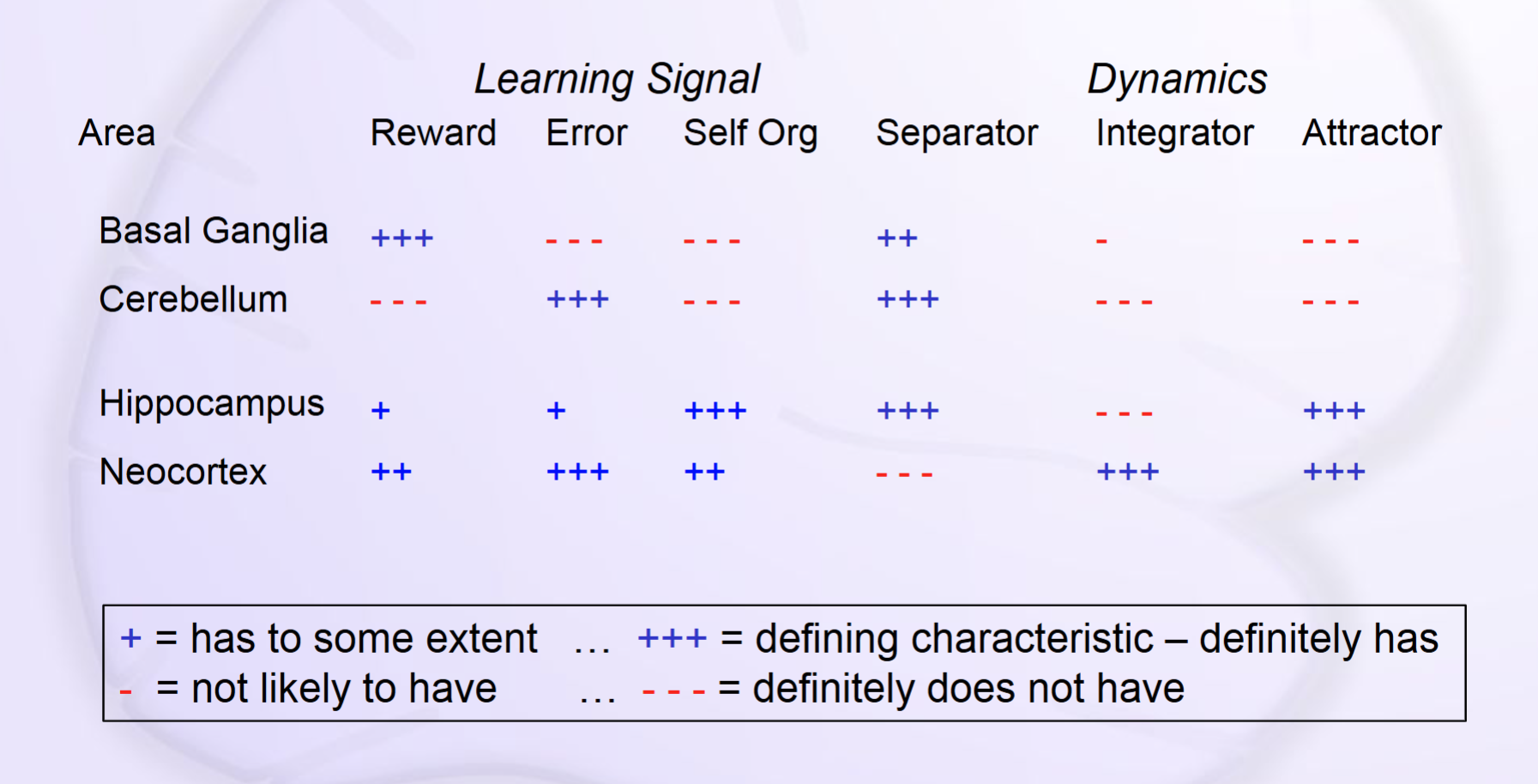
- Note:
- Basal Ganglia = Reward Driven Learning
- Cerebellum = Error Driven Learning
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
- Funny analogy
Basal Ganglia and Action Selection
Basal Ganglia: Brakes on brakes circuitry
- Dopamine burst reinforces Go, dopamine dip reinforces no go
What drives the dopamine signal?
- Reward Prediction Error (RPE) = Reward received - reward expected
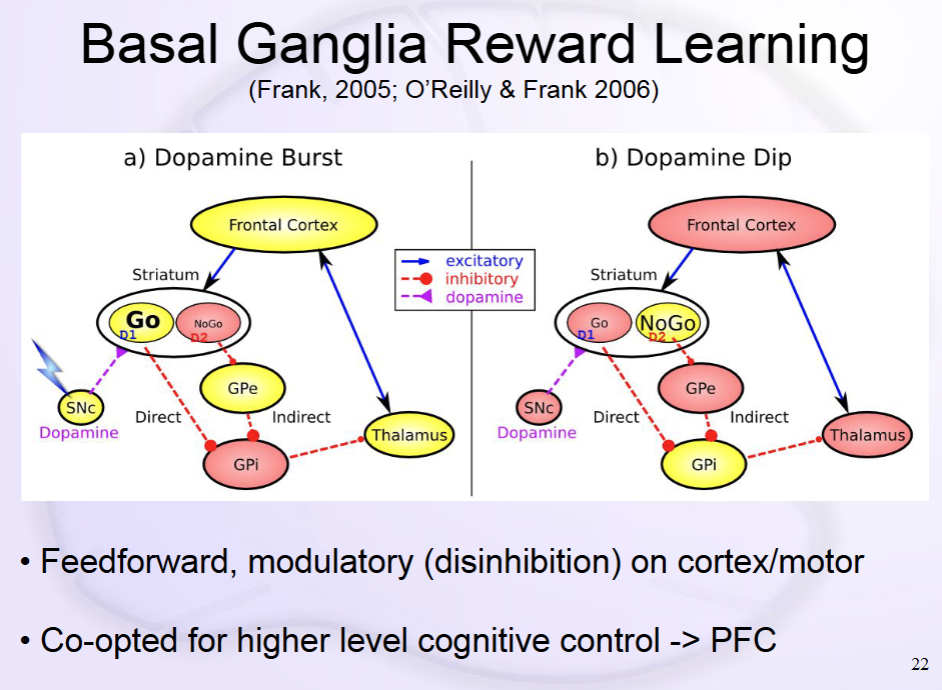
Go Pathway
Positive dopamine reinforces Go
No Go Pathway
Negative dopamine reinforces No Go
🧪-> Example
Explain to the person on the bus: How do you choose what actions to take? Pick a particular decision you might face. Your answer should include dopamine, learning, and the basal ganglia Go and No Go pathways.
In motor learning, we learn how to make decisions based on the interactions between different pathways in our brain, which we call the Go and No Go pathways. This comes up all the time, with something as simple as picking up a cup. We might instinctively want to grab it with our open hand because we're thirsty, but if we know the cup is really hot we might wait before grabbing it because our No Go pathway is active and telling us not to. Once its cooled down and our No Go pathway isn't as active, our Go pathway action might be taken and we might grab the cup. These pathways are reinforced with the neurotransmitter dopamine, which might help us learn if it was a good decision to grab the cup and take a drink. If the cup turned out to still be hot, we might get low dopamine and in the future have learned to not grab it quite yet. If it wasn't, our dopamine might be higher and our Go pathway would be reinforced.
🔗 -> Links
Resources
- Put useful links here