📗 -> Lecture Date: Name
[Lecture Slide Link]
🎤 Vocab
❗ Unit and Larger Context
Super late
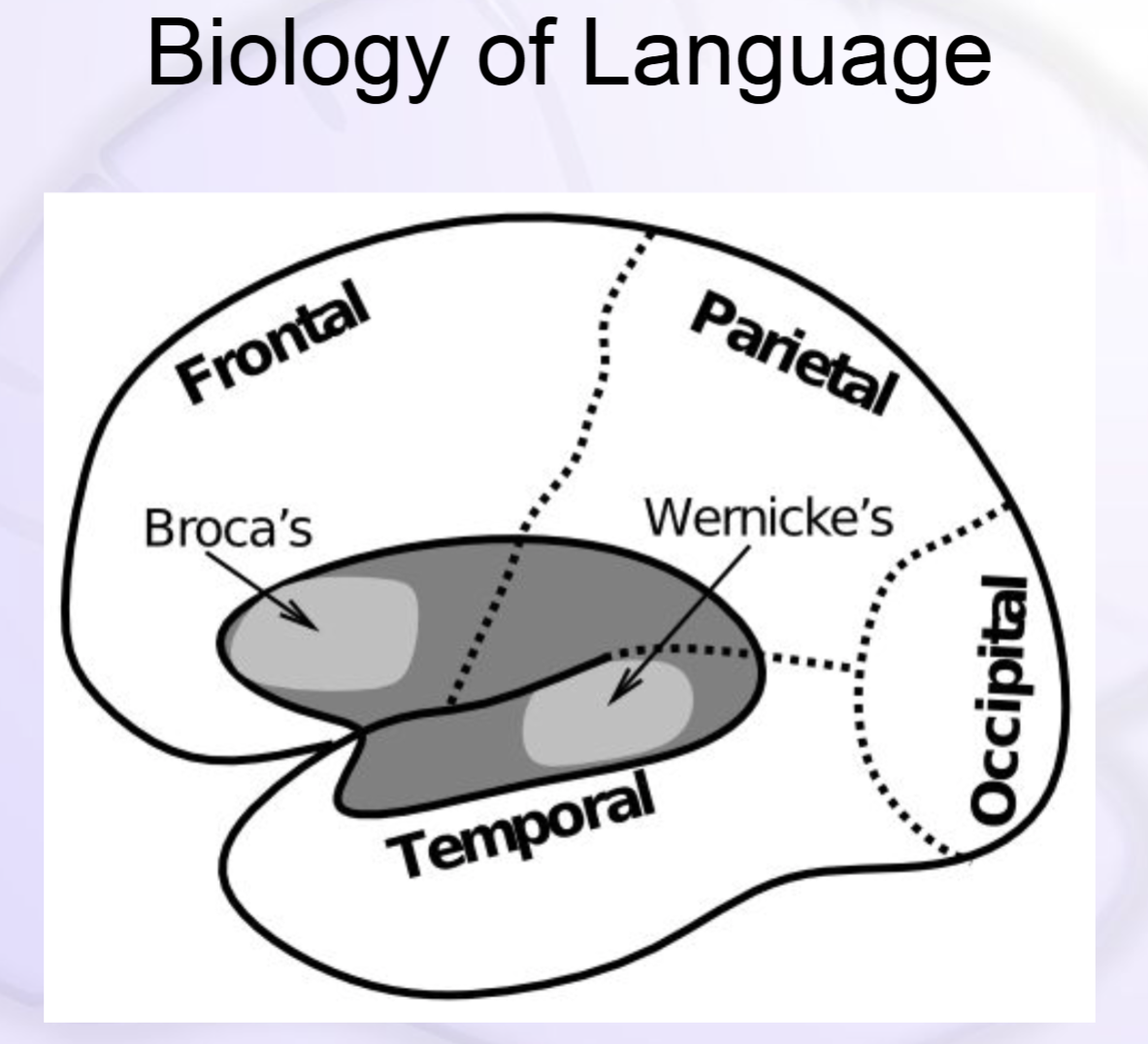
Cool Image
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
Word Statistics
Can you infer word meaning from the company it keeps?? − Yes! Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA)
Just like V1 RF model – extract statistical structure from natural correlations in language
Language Models
Where do we get meaning? (semantics)
- A network “reads” every paragraph in a textbook, acquiring a surprisingly good semantic understanding by noting which words tend to be used together or in similar contexts.
Reading (orthography->phonology) - A network learns to read and pronounce nearly 3,000 English words, and generalizes to novel nonwords (e.g., “mave” or “nust”) just like people do.
Dyslexia - Damaging a reading model simulates various forms of dyslexia – based on orthography, phonology, semantics
Sentences - A network learns to encode syntax and semantics in an integrated Gestalt hidden layer
🧪 -> Examples
Odd quiz based on which is the “best” choice. Model is presented with this quiz in way where a is always the best model.
Multiple Choice Quiz
- neural activation function
a. spiking rate code membrane potential point
b. interactive bidirectional feedforward
c. language generalization nonwords - transformation
a. emphasizing distinctions collapsing differences
b. error driven hebbian task model based
c. spiking rate code membrane potential point - bidirectional connectivity
a. amplification pattern completion
b. competition inhibition selection binding
c. language generalization nonwords - cortex learning
a. error driven task based hebbian model
b. error driven task based
c. gradual feature conjunction spatial invariance
iClicker Quiz
- object recognition
a. gradual feature conjunction spatial invariance - attention
b. competition inhibition selection binding - weight based priming
a. long term changes learning
weight based priming is long term changes to learning
activation based priming is short term changes
this is activation based -> b. active maintenance short term residual - hippocampus learning
b. fast arbitrary details conjunctive
this contrasts with the cortex that learns via: c. slow integration general structure
🔗 -> Links
Resources
- Put useful links here