Topics
Lecs
- Course intro
- Os-intro
- Syscalls
- Os-structure (up to page 8 ‘dynamic/static libraries’)
“Midterm Menu”
- OS intro - 1 q
- Syscalls - 4 q
- OS Struct - 1q
Review: - Especially all the code example related to syscalls and file descriptors
OS Intro
Bare minimum of computer:
- CPU, Interrupts, Timer, Interconnect, Memory, UART/Serial Controller, HDD/SDD Controller, UI, Persistent Storage
Processor:
- Control Unit, Register, ALU, Memory Access
Memory: - Addressable bytes that can hold numerical values
- Speed:
- Registers > Cache > RAM/Main Mem > Second Level Storage
I/O:
- Registers > Cache > RAM/Main Mem > Second Level Storage
- Made up of controller and an actual device
OS Roles:
- Referee - resource allocation, isolation, communication
- Illusionist - resource virtualization: mask specificities/scarcity of resources, mask hardware failures
- Glue - Communication services: APIs to hardware, IO operations, filesystem, etc.
Design Principles:
- Reliability
- Security
- Portability
- Performance
System Calls
Categories of libc functions:
- No priveledged operations
memset- only needs access to buf
- Always need to request priveledged operations (syscalls) from OS
open- needs: verification of a file existing, check if user has access, actually reading file
- Sometimes need priveledged ops
printf- prints to stdout, flushing buffer requires OS to write chars (use of syscall write() )
syscalls - Secure API between user applications and kernel
- Categories: Process management, files/dirs, pipes, signals, mem management
Process - a program in execution
- Identified by a PID (process ID)
- Process runs its own mem space
- Process is represented in the OS by a PCB (process control block)
- Data structure storing info about process
- PID, state, CPU register copies for context switching, open files, etc.
PCB
-----------|
PID=1 |
state |
ctxt |
files |
... |
------------
Main functions/syscalls
- Process creation execution
fork(),exec()exec[lv]p?e?- list vs vector ([lv]), path (p), environment (e)
- Process termination
exit()- End running processwait()/waitpid()- Wait for a child process and collect exit code
- Process identification
getpid()- get process PIDgetppid()- get parent process PID
VFS - Virtual File System
Other syscalls:
- File interaction
open(), close(), read(), write(), lseek() {move file offset}
- File descriptor management
dup2(source, target)- duplicate file descriptor
- File characteristics
stat()/fstat()- get file status
- Directory traversal
getcwd():get current working directorychdir(): change directoryopendir(): open directoryclosedir(): close directoryreaddir(): read directory
File Descriptors:
- Table of open files per process, indexes in PCB
- 0: STDIN
- 1: STDOUT
- 2: STDERR
Signals:
- Many different signals, form of interprocess communication
- Segmantation fault, signal interrupt, etc
Main related functions/syscalls:
Sending signals
raise(): Send signal to selfkill(): Send signal to other processalarm()/setitimer(): Set timer for self- Receive signal (SIGALRM/SIGVTALRM) when timer is up
Blocking signals
- Receive signal (SIGALRM/SIGVTALRM) when timer is up
sigprocmask(): Examine or change signal masksigpending(): Examine pending blocked signals
Receiving signalssigaction(): Map signal handler to signal- Also
signal()but not recommended
- Also
pause(): Suspend self until signal is received
OS Structure
OS Layers:
- Application
- Libraries
--- Divides User from Kernel --- - Portable OS Layer
- Machine-dependent layer
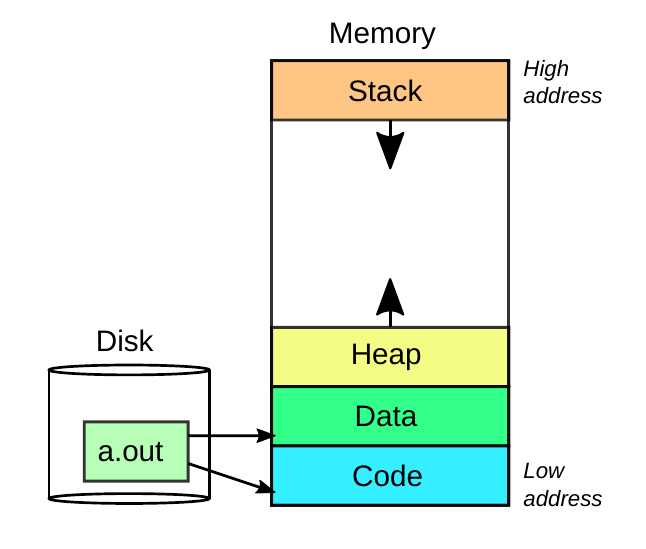
Libraries:
- Static vs Dynamic
Application Compilation:
- GCC
- Preprocessor (cpp) transform program before compilation
- Compiler (cc) compiles a program into assembly code
- Assembler (as) compiles assembly code into relocatable object file
- Linker (ld) links object files into an executable