Dataview
LIST
FROM #Collection
WHERE file.name = this.Entry-For📗 -> A Broad Overview of the Event-Related Potential Technique
🎤 Vocab
ERP - Event-related potential
EEG - Electroencephalogram
ERP components - A noticeable reaction in ERP signal. In themselves they don’t necessarily indicate anything, but smart detection of them can give hints to neural underworking.
PET - Positron Emission Tomography
fMRI - Functional Magnetic Imaging
MMN - Mismatch Negativity component
a relatively specific measure of PSPs produced by the binding of glutamate to N -methyl- d -aspartate (NMDA) receptors
❗ Information
International 10/20 System:
- System naming:
- Each electrode site named one or two letters to indicate the general brain region
- Given a number to indicate the hemisphere (odd for left and event for right)
- Larger numbers indicate a larger distance from the midline
- Lowercase z is used to represent the number zero, meaning on the midline
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
Data processing <-> Treating an illness
Treatments have side effects (ibuprofen can cause dizziness).
ERP processing treatments can distort onset/offset times, cause unpleained peaks, and more
Apply treatments in ways that minimizes side effects
- One example of a defined ERP signal is a negative signal. A CNV (contingent negative variation) is eliceted when subjects have a reason to ignore a stimuli (ignore the first flash and react the second). A noticeable negative voltage will be observed, completely seperate from sensory signals. This is an example of a ERP signal showing hints of cognition.
- P300 - The most famous component. It happens when an expected stimulus is shown. Now frequently called the P3.
- Most prevalent on the Pz electrode (on the midline of the parietal lobes)
- ERPology (Luck & Kappenman, 2012a), a book he wrote describing different existing ERP components.
- ERP is one of our best ways for observing temporal phenomenons in the brain. The temporal resolution of other methods can’t compare to it.
N170 Component
A face-related component that typically peaks around 170 ms after stimulus onset and is largest over ventral areas of visual cortex
- Response is bigger for faces than for non faces
- Allows us to tell that the brain can distinguish faces from other objects within 150ms
Neural Origins of ERPs
ERPs originate as postsynaptic potentials (PSPs)
PSP vs Action Potential (AP)
Action potential
- Is formed when stimulus is high enough, and a large depolarization is induced at the axon hillock
- All or none
- Large depolarization
PSP - Occurs when neurotransmitters bind to receptors, resulting in a change in the membrane potential
- Can be gradual, EPSP or IPSP gradually changing potential
- Measured in 1-5mV
Forming a dipole
Changes in membrane potential create a tiny dipole, and when summed are measurable by EEG
- Requires 1000s of similarly oriented neurons
Pyramidal cells are oriented perpendicularr to the cortical surface and can be added together
Designing a witty ERP experiment
Subtracting differences between normal trials and trials of interest can help to remove uninteresting signals from sensory processing. See Figure 1.4
You can use the differences to draw conclusions about what is and isn’t occurring“The best solution is often to figure out a clever experimental design in which isolating and localizing a given ERP component is not necessary to distinguish between competing hypotheses (see the discus- sion of component-independent experimental designs in chapter 4).”
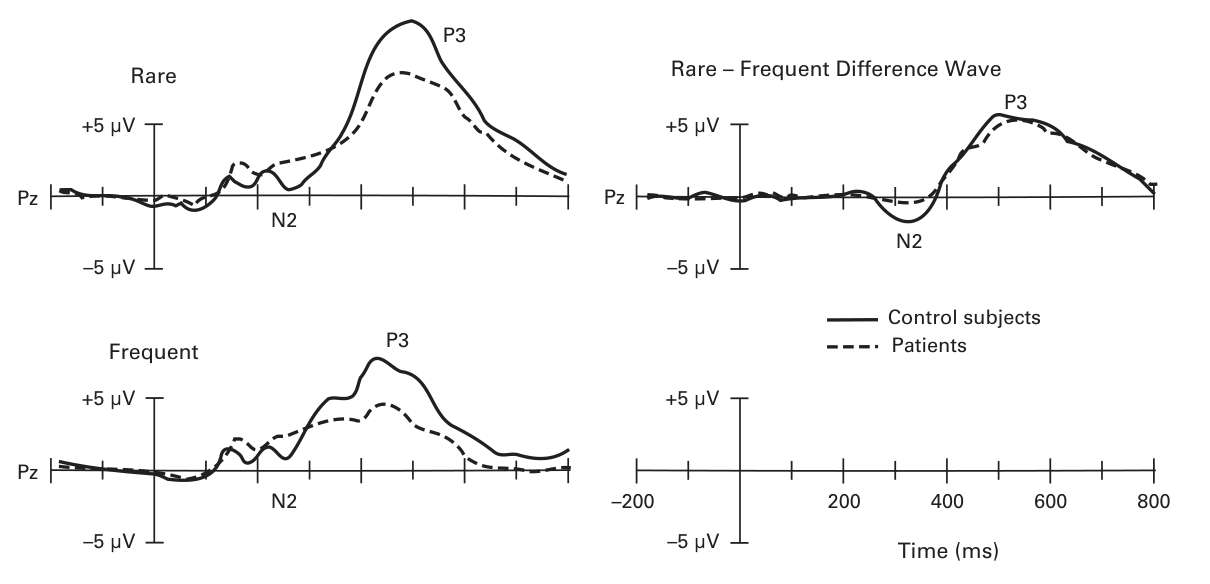
- Figure 1.4
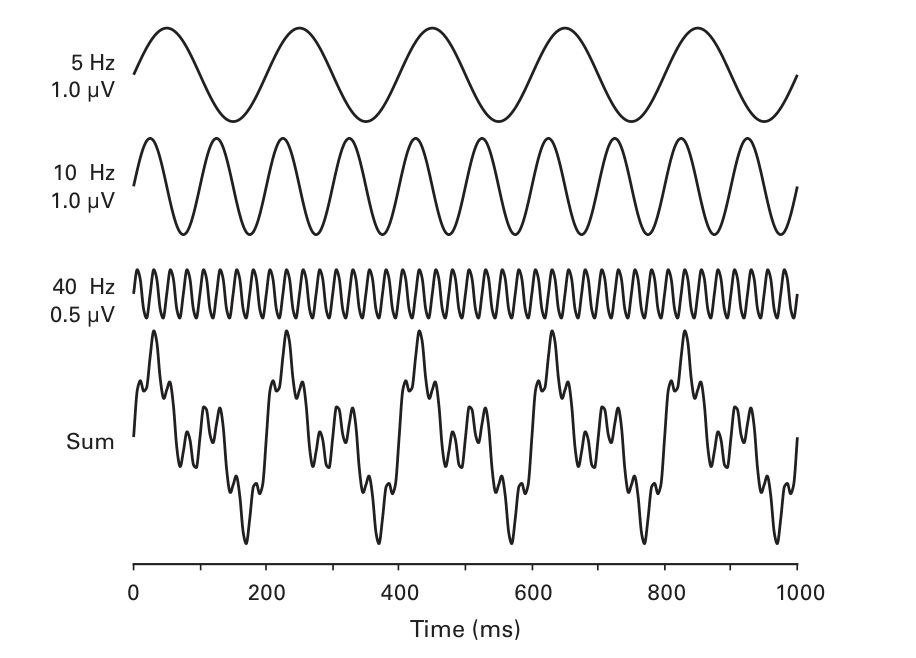
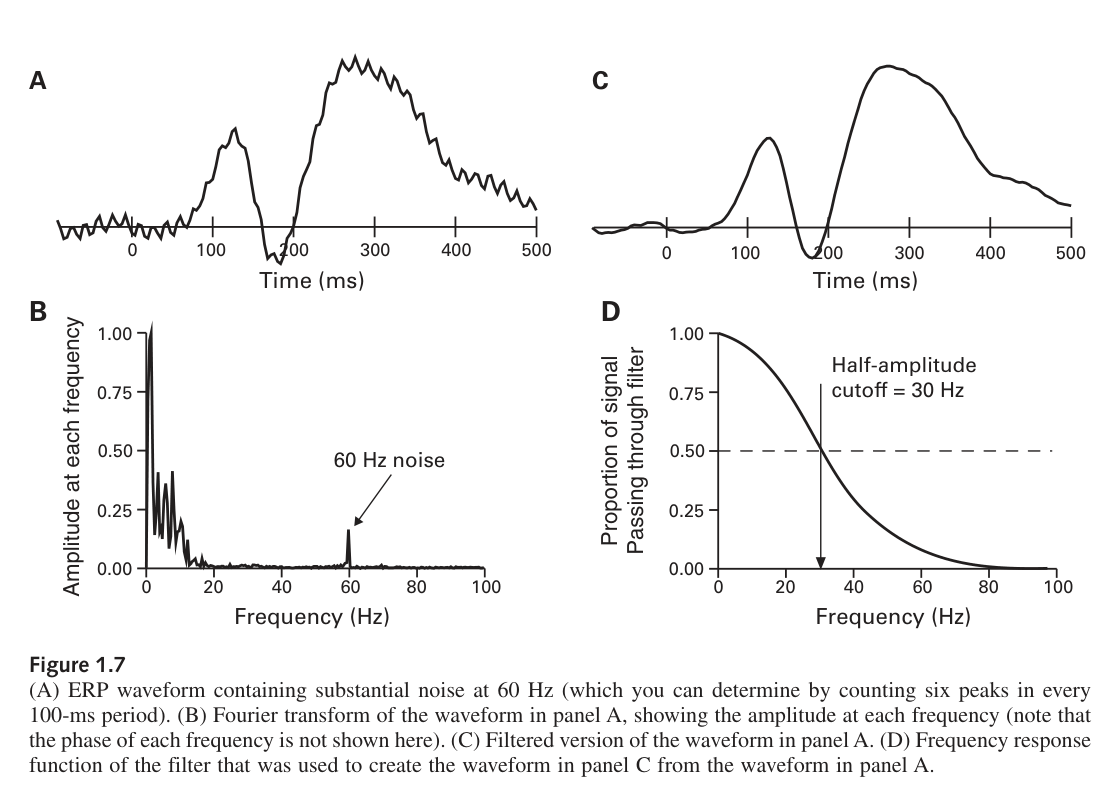
EEG Example
Link to original
The above is a demonstration of what the FT can accomplish. The FT aims to deconstruct a waveform into a sum of sine waves. However, this does not imply the original waveform actually contained the frequency, just that the FT uses it to properly deconstruct.
Computing Average Waveforms
For large ERPs (P3), clear results can be obtained within 10-50 trials
For smaller components (P1), usually need 100-500 trials of each type to see clear differences.
Waves are denoised in O(logn) time
🧪-> Example
- ERP Methodology - EEG recordings require one or more active sites, along with a ground electrode, and a reference electrode.
- EEG is amplified massively (x20,000) then converted into digital form for storage on a digitalization computer.
- Naturally, EEG signals are analog and continuous, they are sampled and made digital and discrete.
- Averaging out signals: The hope is that this will cancel out signals unrelated to the trial (as they will vary inconsistently) leaving only the signal due to the experiment.
- EEG is amplified massively (x20,000) then converted into digital form for storage on a digitalization computer.
🔗 -> Related Word
- Link all related words