Dataview
LIST
FROM #Collection
WHERE file.name = this.Entry-For📗 -> Chapter 4: Learning
🎤 Vocab
Synaptic Plasticity - Modification of synaptic weights through learning
Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity
Long Term Potentiation (LTP)
Long Term Depression (LTD)
Hebbian Learning - The idea that cells that fire together, wire together
❗ Information
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
Error Driven Learning
Uses contrasts between expectations and outcomes
Neuromodulators such as dopamine, norepinephrine and acetylcholine likely play an important role in modulating this form of learning
Plasticity
Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlu) also play an important role in synaptic plasticity
These receptors respond to neurotransmitters and modulate AMPA
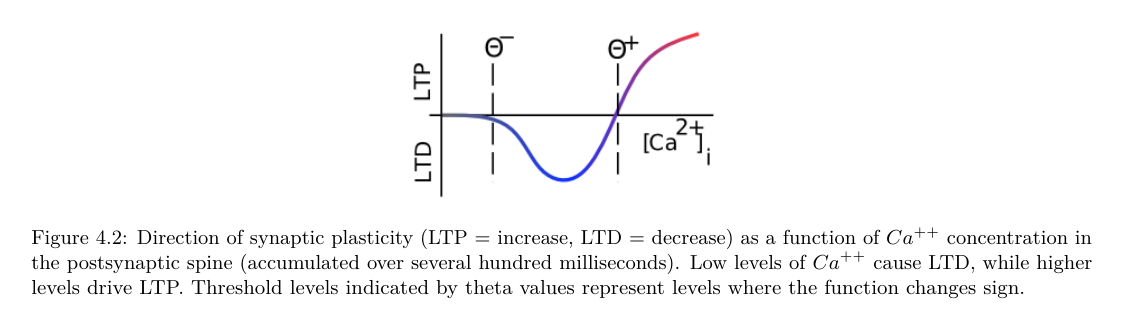
Two large forms of plasticity, LTD and LTP. They both effect AMPA efficacy long term.
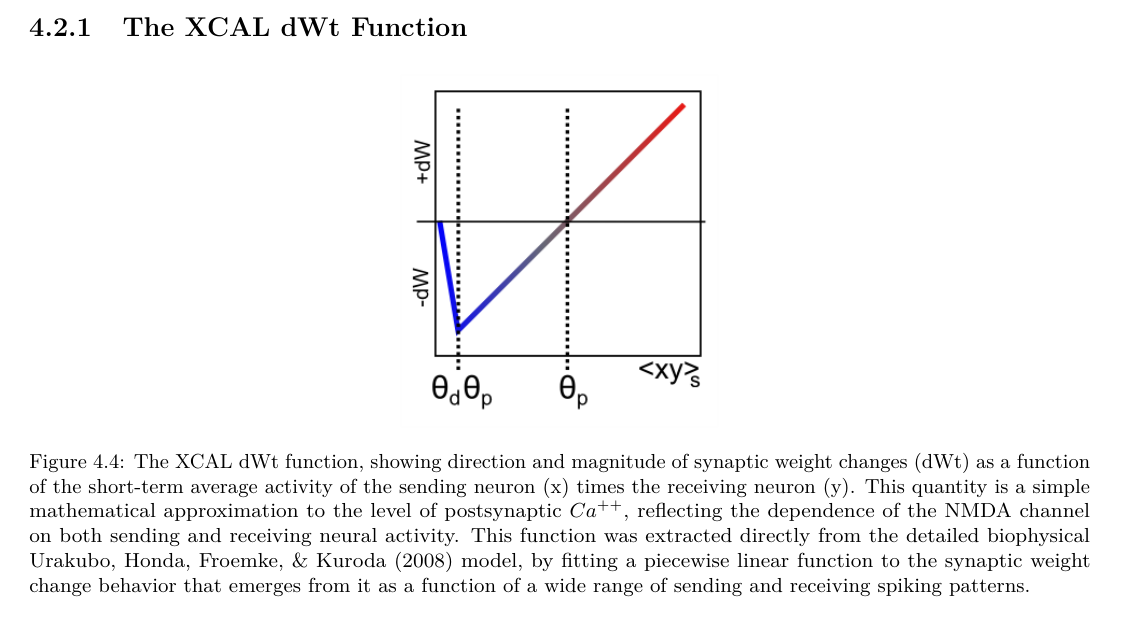
XCAL
XCAL Model - A model used in the eXtended Contrastive Attractor Learning rule.
- Highly biologically detailed
- Closely resembles the BCM learning function
Self-Organizing Learning
Reliant on the ability to spread around neural activity.
It enables neurons to more efficiently and effectively cover the space of things to represent.
- Inhibitory Competition
- Rich get Richer positive feedback loop
- Lets the most important neurons have more impact
- Homeostasis
- Prevents the rich get richer from spiraling out of control
Framework for Error-Driven Learning
Neurons go through cycles of expectation and outcome
- A Trial lasts 100 msec (10 Hz, alpha frequency), and comprises one sequence of expectation — outcome learning, organized into 4 quarters.
- Biologically, the deep neocortical layers (layers 5, 6) and the thalamus have a natural oscilla-tory rhythm at the alpha frequency. Specific dynamics in these layers organize the cycle of expectation vs. outcome within the alpha cycle.
- A Quarter lasts 25 msec (40 Hz, gamma frequency) — the first 3 quarters (75 msec) form the expectation / minus phase, and the final quarter are the outcome / plus phase.
- Biologically, the superficial neocortical layers (layers 2, 3) have a gamma frequency oscillation, supporting the quarter-level organization.
- A Cycle represents 1 msec of processing, where each neuron updates its membrane potential according to the equations covered in the Neuron Chapter.
Combining Learning
One analogy that may prove useful is that error-driven learning is like socialist economics — it requires all the different layers and units to be working together to achieve common goals, whereas self-organizing learning is like free market economics, emphasizing local, greedy actions that somehow also benefit society as a whole, without explicitly coordinating with others.
In the brain, maybe a centrist view is more accurate. Both styles have their place.
🧪-> Example
Reactions need to include:
- Big picture: general reaction
Did you generally find the overall content understandable or compelling or relevant or not, and why, or which aspects of the reading were most novel or challenging for you and which aspects were most familiar or straightforward?)
I liked the introduction into computational learning mechanisms. It's very interesting to me how much overlap there is with machine learning like deep learning, especially the introductions into backprop and hidden layers. I still don't have a great handle on the math and I'd like to see some of the models/rules in action. Particularly the LTD/LTP curve, that one is particularly tricky to me for whatever reason, I can't tell if LTD is induced if the stimulus is at its lowest, or at a middle value.
- Specifics: specific reaction to one aspect of the reading
Did a specific aspect of the reading raise questions for you or relate to other ideas and findings you’ve encountered, or are there other related issues you wish had been covered?)
Error driven learning seems very similar to the reward prediction error that I've encountered before, but it also seems different. I'm wondering how error-driven learning is effected in the brain aside from the RPE. Especially in pathways like visual expectations that don't seem like they would be as involved in the dopamine pathways.
🔗 -> Links
Resources
- Put useful links here
Connections
- Learning