Review Seshes
wed 3/12 - Link
Content Review:
- Suffix Trees
- Optimality Recurrence
- BLAST Hash Tables
- Additive Matrix
- UPGMA
thursday 3/13 - Link
Content Review:
- MT 2
- 5b part 3
- part 2d
- Writing pseudo code?
- Light perl scripting?
friday 3/14 - Link
saturday 3/15 - Link
ECS124-Final-Prep 2025-03-17 16.03.31.excalidraw
Content
Labs:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Midterm 1
Sequence alignment
- Global / Local / Semi-global
- Global: Needleman–Wunsch algorithm
- Local: Smith-Waterman
- Sem
- Biological uses for each one
- Longest common substring and subsequence
- How do LCS and global alignment relate?
Blast
Recurrence relations
Runtime analysis (Big-O)
Writing code - Perl and Python
- How do LCS and global alignment relate?
- Working with files, opening/writing/reading
- Regex, matching and replacing
Midterm 2
Clustering and Trees
Bayes Method
K-means
De Bruin Graph
- Genome assembly?
Suffix Trees - Common sequences between paths
Post Midterm 2
Hierarchical Clustering
- UPGMA
- Nearest neighbor
- General probability of a path and model combo.
- Viterbi algo
Ultrametric Tree
-
A tree where all leaves are equidistant from the root
-
In an ultrametric tree, the two longest distances among any three points must be identical.
-
- There is no unique maximum, it will repeat
-
Matrix M is only ultrametric if the maximum value in any 3 rows is not unique
UPGMA - Unweighted Pair Group Method with Arithmetic Mean -
Go through a matrix combining rows/columns as you combine nodes (species/taxa)
-
Combines the ‘closest’ neighbors iteratively
- A and B make node AB combined
-
With an ultrametric matrix, it will create a tree that is ultrametric and additive
-
Additive trees
- Use the four point test to test for additivity
Transclude of ECS124-L14-2025-03-04-18.33.05.excalidraw
- However, can be difficult, because for a matrix with 5 points, you need to test 5 groupings (5 choose 4 = 5)
- Use the four point test to test for additivity
-
Jukes Cantor
Nearest Neighbor?
Neighbor Joining
Hidden Markov Models
Viterbi
- The viterbi algorithm is a Dynamic Programming algorithm that uses a hidden markov model and its transitions to find the most likely path to have produced emissions. It iteratively goes through the most likely thing to have emitted a character at every stage, and finds probability for both models
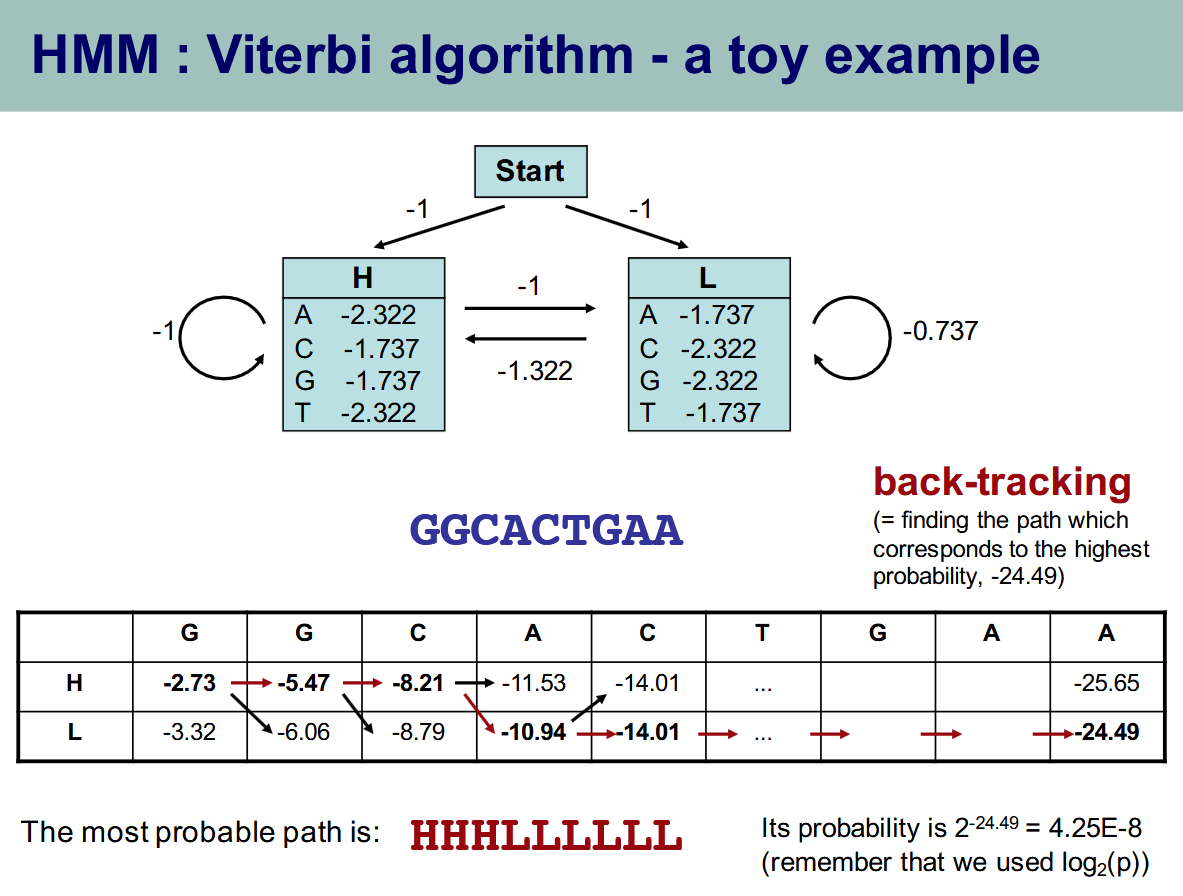
- Uses the max probability of arriving to a state, factoring in the immediately preceding state. Linear time, DP, very cool!
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 8 | 5 | 4 | |
| B | 7 | 3 | ||
| C | 2 | |||
| D | ||||
| Nearest joining: | ||||
r(i) = d(A,C) + d(B,C) + d(C,C) + d(D,C)
- 6+7+0+2 = 15 / 2 = 7.5
r(j) = d(A,D) + d(B,D) + d(C,D) + d(D,D) - 4+3+2 + 0 = 9 / 2 = 4.5
D(C,D) = 2 - 7.5 - 4.5 = -10
UPGMA
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| B | 0 | 4 | 6 | |
| C | 0 | 6 | ||
| D | 0 |
Heigh of AB is the average of their cluster distance
dist(AB,C) = ( D(A,C) + D(B,C) ) / 2 = 4
dist(AB,D) = ( D(A,D) + D(B,D) ) / 2 = 6
| AB | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AB | 1 | 4 | 6 |
| C | 0 | 6 | |
| D | 0 | ||
| D(ABC, D) = ( D(AB, D) + D(C, D) ) / 2 = 6 |
- Distance between old node (AB) and new node (C) to D
| ABC | D | |
|---|---|---|
| ABC | 2 | 6 |
| D | 0 |
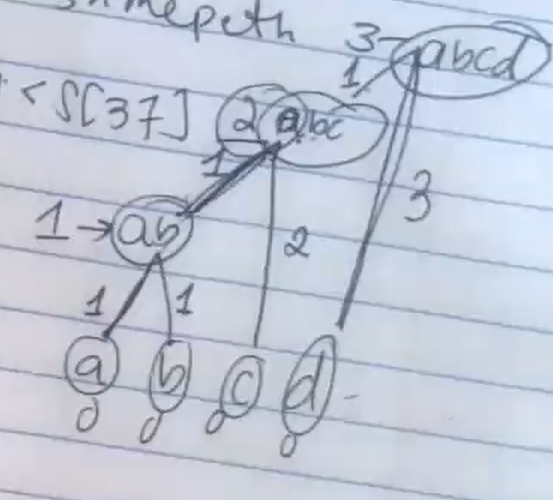
- Makes this tree at the end.
- Final height is 3