📗 -> 04/02/25: NPB163-L2
[Lecture Slide Link]
🎤 Vocab
❗ Unit and Larger Context
Small summary
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
Practice:
How to:
- Extracellular recording?
- Electrode
- Intracellular recording?
- Insert a —
- Patch clamp, seal the membrane
- What do we measure?
- Membrane potential
- EPSP / IPSP
- ECoG / iEEG
- Electrode grid placed on the surface of the brain
- Measures population activity
- Optical Imaging
- There is intrinsic / voltage sensitive dye / calcium sensitive dye
- Intrinsic - Measure reflectance of the light, measure oxygen consumption of area
- Indirect measure of activity
- There is intrinsic / voltage sensitive dye / calcium sensitive dye
Today’s Class - Non-invasive
EEG / MEG / fMRI
EEG
Noninvasive measure popular in cognitive neuroscience
EEG signal is an aggregate signal that has been heavily filtered (volume conduction, skull); localizing the source of a signal component is difficult; temporal resolution is good
How?
- Positive charge gets into dendrites, leaves negative charge outside
- Creates a dipole:
- Positive on cell body
- Negative on cell dendritic synaptic terminals
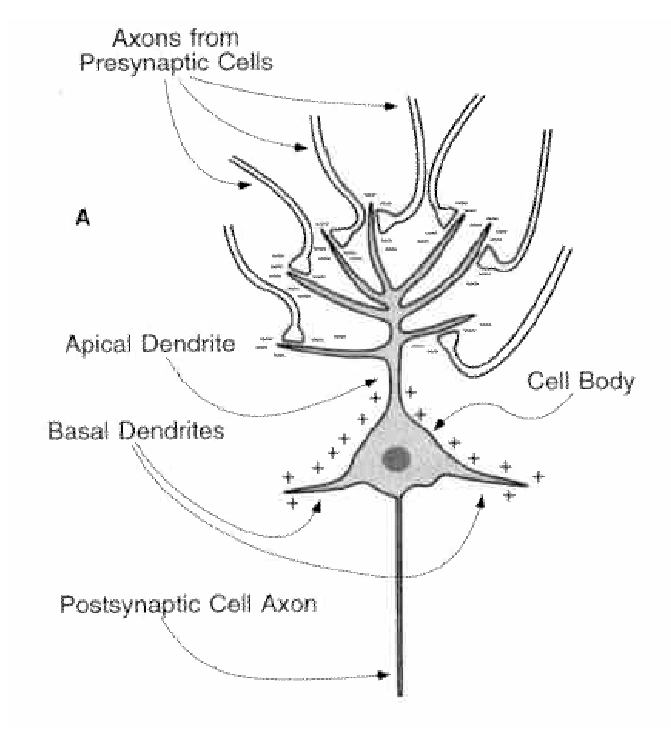
- Creates a dipole:
EEG is primarily used to measure either evoked potentials or oscillatory activity at various frequencies
MEG
- On top of measuring electric field, we can measure the magnetic field.
- With MEG, we measure the magnetic field around the head generated by eletric activity in the brain
- Less popular than EEG due to its equipment (expensive, bulky)
- Better spatial resolution than EEG, magnetic field less distorted by skull and scal than the electric field
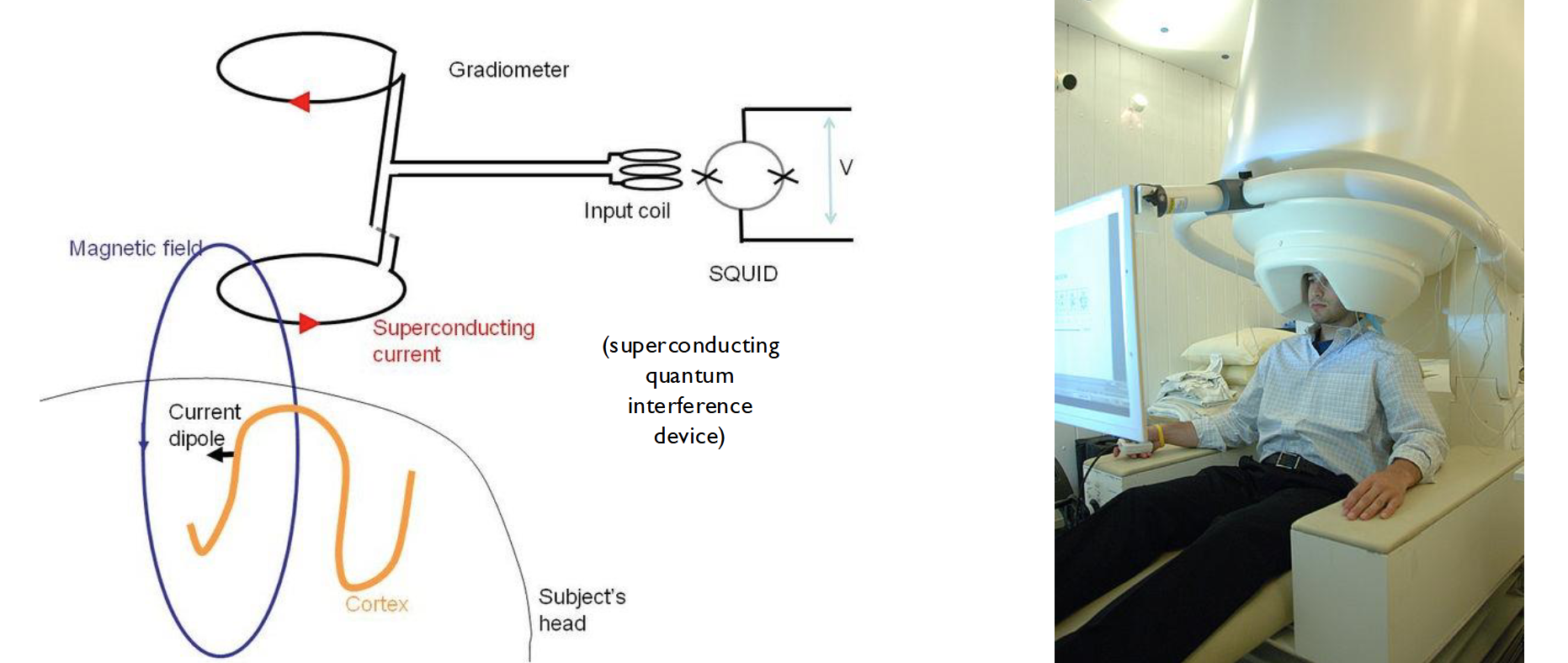
Apparently there's a lot of online resources about MEG data?
fMRI
- fMRI is probably the most popular technique for noninvasively measuring neural actvity in - cognitive neuroscience.
- It is an indirect measurement of neural activity, providing a Blood Oxygenated Level Dependency - (BOLD) signal
- A strong static magnetic field (B0) is used to align spins (of, e.g., protons in water or fat in body tissue).
- A radiofrequency (RF) magnetic field (B1) causes spins to flip (transient loss of alignment with B0 field) and to phase-synchronize.
- Signals resulting from the realignment of the spins with the B0 field and from phase desynchronization are measured.
- Gradient fields are used to make the measurement spatially selective
T1 and T2 components:
- T1 spin-lattice relaxation time?
- Used for anatomic imaging
- T2 spin-spin relaxation time?
- More measuring how synchronized different protons are
- important component for fMRI; measurement of local field inhomogeneities resulting from the paramagnetic properties of deoxyhemoglobin
Time delay:
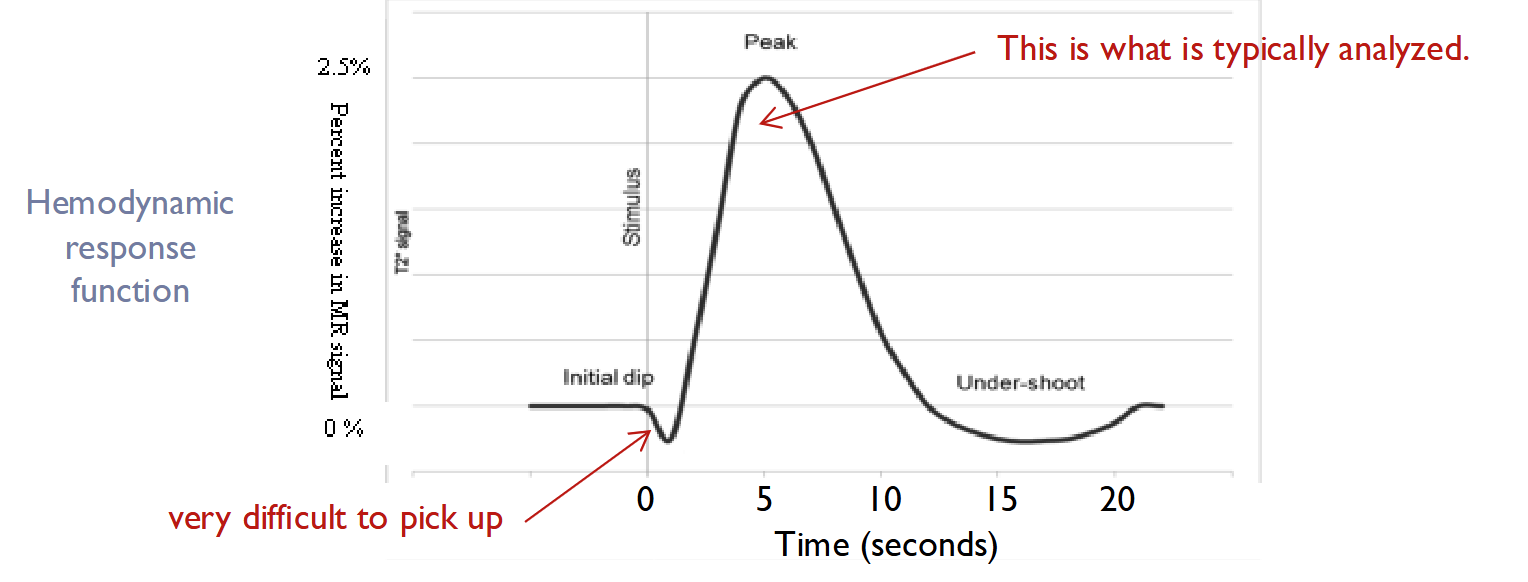
- Intrinsic imaging will analyze the initial dip, while fMRI will measure the hemodynamic peak
- Also be careful of what we are actually measuring:
- BOLD correlates with energy demanding activity. This is not necessarily spiking activity.
- Strongly influenced by dendritic activity
Check the lecture slides 40-41 for technique tables. Very helpful
Interpreting Neural Activity
We cannot assume causation, merely correlation a lot of the time.
Easy example:
- Knee reflex:
- You’ll see activation in both somatosensory cortex, and the reflex.
- However, they are not linked. It is the sensory nerve that invigorates both. This causes linked/correlated activity, but no causal connection.
Establishing a causal relationship requires manipulation of neural activity.
- Traditionally, this was done through lesion studies.
- Phineas Gage e.x.
- They used his lesion to link the prefrontal cortex to self control.
- However, waiting for specific patients is infeasable.
Experimental Lesions:
- Advantage of being able to define location of lesion
- Options to do it surgically or chemically
- However, irreversible
Reversible Inactivation: - Allow study of before / during / and after inactivation.
- Possible chemically
- Possible with an implanted cooling device (cooling chip / cryoloop)
More Stim
Microstimulation
REVIEW
Optogenetic Stimulation
Introduce molecules that can be light-activated into the cell membrane in order to depolarize or hyerpolarize the neuron
- Channels for both:
- Depolarization (light gated leak channel)
- Channelrhodopsins
- Hyperpolarization (active pumps)
- Halorhodopsins
- Archaerhodopsins
Typically done by creating transgenic animals or viral-based gene delivery
- Depolarization (light gated leak channel)
The advantage of optogenetics is that specific cells can be genetically targeted such that only a particular type of neurons is affected by the stimulation
The disadvantage is with viral-based delivery, the viruses used as vectors have their own cell specificity
Questions?
- Review optical imaging
- What is T3 measuring?
- Hell whats is T2 measuring
🧪 -> Refresh the Info
Did you generally find the overall content understandable or compelling or relevant or not, and why, or which aspects of the reading were most novel or challenging for you and which aspects were most familiar or straightforward?)
Did a specific aspect of the reading raise questions for you or relate to other ideas and findings you’ve encountered, or are there other related issues you wish had been covered?)
🔗 -> Links
Resources
- Put useful links here
Connections
- Link all related words