📗 -> 04/21/25: NPB163-L7
🎤 Vocab
❗ Unit and Larger Context
Started from “Mapping receptive fields (2)”, page 21
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
Simple Cells and Complex Cells
Simple Cells - Spatial Frequency tuning
Complex Cells - Orientation tuning, and movement
Mapping Receptive Fields (3):
White noise stimulus and reverse correlation
Find the most active random patterns for a neuron, and average them?
- Get out almost a heatmap for the receptive field
- However, the prior for this is that cells are independents.
- For complex cells that need relationships between cells, it won’t capture relationships
Neural Maps in V1
1. Retinotopic Maps
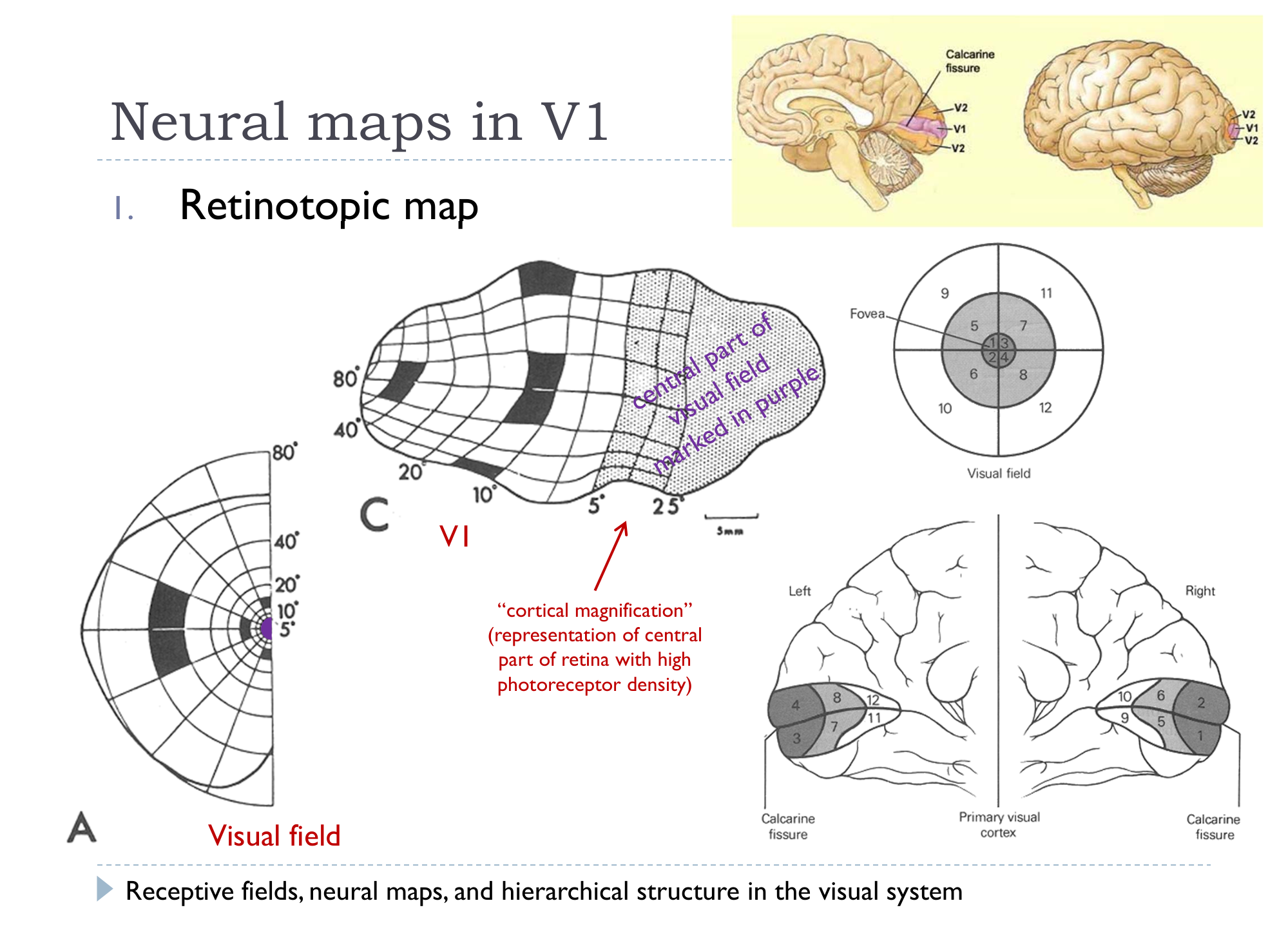
2. Orientation preference maps
Neurons with similar orientation preferenecs tend to be grouped together, and there tends to be a transition between preferences.
- We see distinct pinwheel centers, where multiple preferences aggregate
Finds round pinwheel centers: - Preference orientation changed smoothly around pinwheel centers
- Tuning width of neurons close to pinwheel center was slightly larger than those of neurons in iso-orientation domains (1 preference)
- 37 vs 31, slightly more general
3. Ocular Dominance Map (inputs to granular layer)
Columns of neurons more responsive to one eye, left vs right.
This dominance pattern does not arise in V2.
Visual Processing Beyond V1
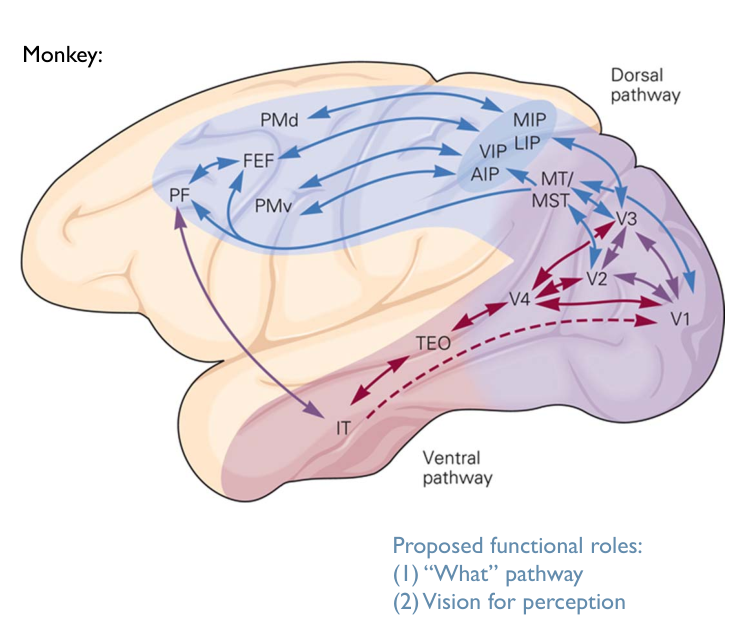
Monkey Brain pic
Proposed functional roles:
- Dorsal Pathways
- “Where” pathway
- Vision for action
- Ventral Pathways
- “What” pathways
- Vision for perception
Human fMRI pic
Motion Processing
MT / MST
Neurons in area MT (middle temporal area; V5) respond selectively to visual motion and are direction tuned
Directional Selectivity can arise from differential delay of input signals:
to detect motion from a to e:
- Stagger delays such that a has the longest delay, and e has the shortest delay
- Only fire when the delayed spikes arrive all at once (due to the delays)
MST (medial superior temporal area) neurons respond to more complex motion patterns involving rotation and expansion/contraction
- Counter/Clockwise rotation
- Contracting in / out (think a parallax effect)
Motion processing
- Perceived vs. local motion: Aperture problem
- Difficult to integrate motion without complete information?
- Review
Barber pole illusion
🧪 -> Refresh the Info
Did you generally find the overall content understandable or compelling or relevant or not, and why, or which aspects of the reading were most novel or challenging for you and which aspects were most familiar or straightforward?)
Did a specific aspect of the reading raise questions for you or relate to other ideas and findings you’ve encountered, or are there other related issues you wish had been covered?)
🔗 -> Links
Resources
- Put useful links here
Connections
- Link all related words