🎤 Vocab
Geometric Deep Learning - This article defines a number of terms well
Curse of Dimensionality: As the number of dimensions to a problem grows, the number of data points necessary to extrapolate a meaningful solution grows exponentially
Kernels: A filter that applies to input data to change its representation (think the outputted hotspots for MNIST PCA)
Representation: The way that data is mapped internally. Think about the warped way that our visual cortex represents an image (more space devoted to fovea)
❗ Important
Categories
Machine Learning is generally categorized into three types: Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, Reinforcement learning
Supervised:
Classification - Discrete Classification
In classification problems the machine must learn to predict discrete values. That is, the machine must predict the most probable category, class, or label for new examples. Applications of classification include predicting whether a stock’s price will rise or fall, or deciding if a news article belongs to the politics or leisure section.
- Predict gender from shoulder / waist sizes.
Regression - Value Prediction
In regression problems the machine must predict the value of a continuous response variable. Examples of regression problems include predicting the sales for a new product, or the salary for a job based on its description.
- Predict house price
Unsupervised:
When we have unclassified and unlabeled data, the system attempts to uncover patterns from the data . There is no label or target given for the examples.
Clustering - Grouping similar things
One common task is to group similar examples together called clustering.
- Group and separate unlabeled songs
Dimensionality-Reduction - Reducing scope
Another common goal of unsupervised algorithms is to reduce dimensions. This can help algorithms to run faster, reduce noise, and can sometimes to make data more interpretable.
Reinforcement-Learning (RL):
Attempting to maximize a goal. Feedback is given to an agent / model.
- Maximize points in a game
Important Concept Links
-
SVD?
-
- Underfitting (too simple to explain the variance)
- Overfitting (forcefitting - Too good to be true)
Snippet Concepts
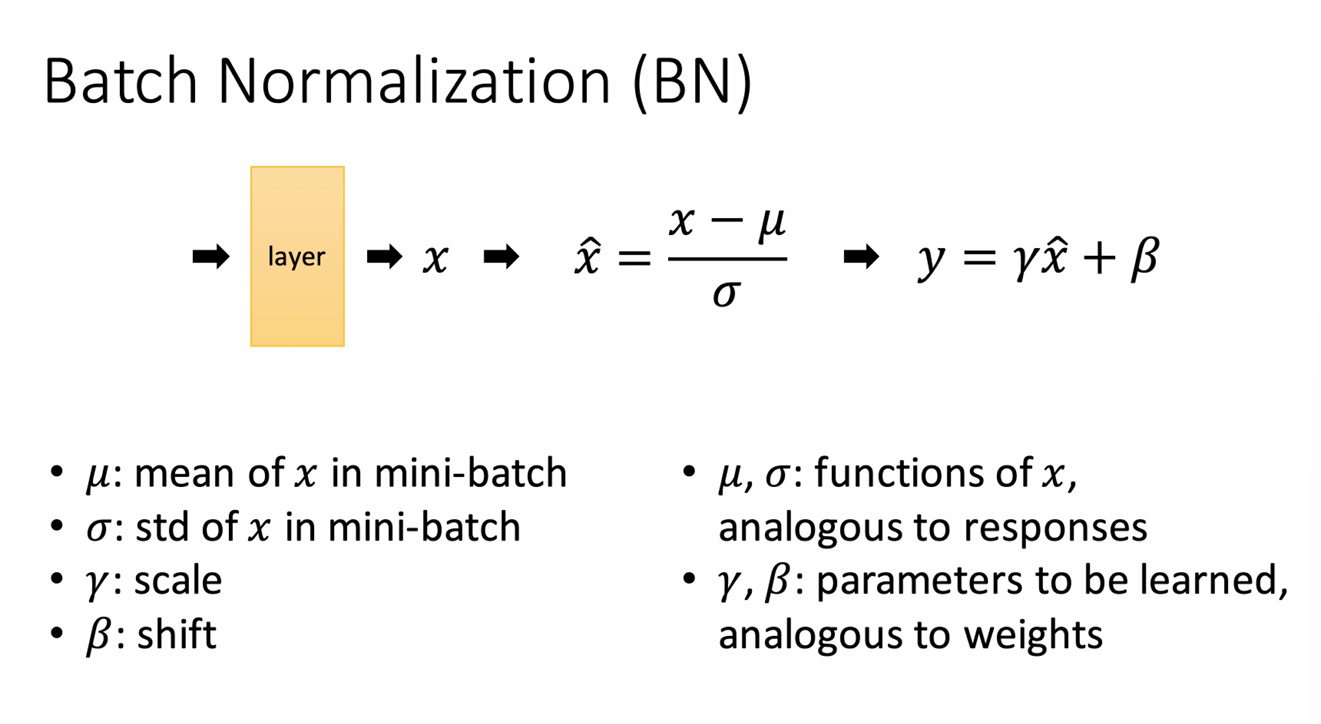
Batch Normalization
Batch Normalization
Two modes of BN:Link to original
- Train mode
are functions of x; backprop gradients - Test mode
are pre-computed on training set
Important Functions for NN Architecture
Important Functions for Architecture:
Normalization
Soft max:
Loss
Loss: Comparing ground truth with the output:
If we’re assuming one hit encoding, we can make the following step:Loss assuming one-hot encoding for ground truth:
Loss for a mini-batch of size N:
Link to original
Specific Interests
Resources
Links
- Transformers as a swiss army knife
- Topology in ML
- Kaggle learn
- Data Preprocessing Medium Series
- Visually Explained YT
- StatQuest Trailer, 2019
- Fast.ai
- http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/
- https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/titanic/code
- https://www.reddit.com/r/learnmachinelearning/comments/fzwvcz/what_is_some_good_ml_beginner_project_i_could_use/