📗 11/5: CNNs Continued
- Slide 16 and after
🎤 Vocab
❗ Unit and Larger Context
Small summary
✒️ -> Scratch Notes
Important Functions for Architecture:
Normalization
Soft max:
Loss
Loss: Comparing ground truth with the output:
If we’re assuming one hit encoding, we can make the following step:
Loss assuming one-hot encoding for ground truth:
Loss for a mini-batch of size N:
Visualizing CNNs
Cool article
Allegories to visual system, layers have more complicated features as you go on
Big ties to explainable AI, there is great value in being able to see what the network is doing under the hood
Strategies for visualizing:
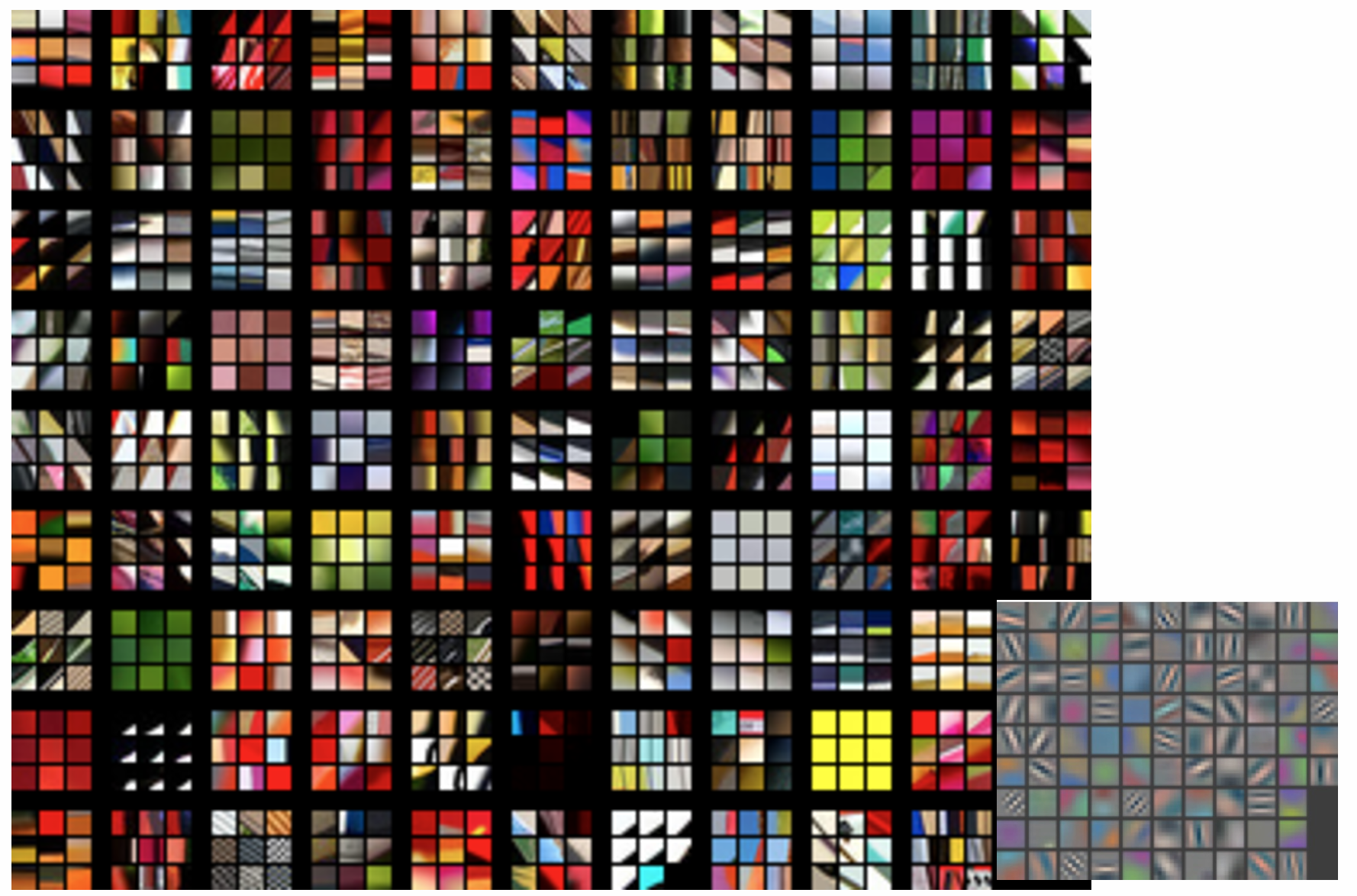
- Visualizing weights, this is very useful for lower level filter extracting physical features. A good use case for this is edge detection
- Visualizing responsiveness. As you get higher leveled, the weights become harder to interpret as they respond to latent features and not direct image qualities. To address this, show each neurons most responsive images. This is done by showing top 9 images
Layer 1
- Simple features, similar to V1 in the brain
Filters in bottom right, Top-9 shown large
Vanishing Gradient Problem
Using gradient descent:
- If one of the layers produces zero (or near zero) gradient, because we multiply the loss together, it will eliminate the gradients in the other layers as well
- Particularly a problem in deep learning, where more layers introduces more possibilities of this happening
🧪-> Example
- List examples of where entry contents can fit in a larger context
🔗 -> Links
Resources
- Put useful links here